Program of Single Cell Omics Beijing 2022.
Notes from Program of Single Cell Omics Beijing 2022.
- Opening
- Session 1
- Session 2
- Bart Deplancke: Engineering Next-generation Single Cell Phenomics Technologies
- Rickard Sandberg: Scalable Full-length scRNA-seq for Temporal Analyses of Transcription and Dissections of Cell States and Subtypes
- Angela Ruohao Wu: Multi-step Single-cell Multi-omics Methods for Simultaneous Dissection of Phenotype and Genotype Heterogeneity from Frozen Tumors
- Guoji Guo:Mapping Cell Landscapes at Single cell Level
- Chenghang Zong: Total-RNA Based scRNA-seq Allows Genome-wide Identification of Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Regulation
- Section 3
- Ning Jenny Jiang: High-throughput and High-Dimensional Single T Cell Profiling
- Yanyi Huang: Improving the Information Efficiency for Fast and Spatially Resolved Sequencing
- Fuchou Tang: Single Cell Omics Sequencing Technologies: The Next Generation
- Zemin Zhang: Dynamic Changes of The Tumor Micro-environment During Immunotherapies
- Xiaoqun Wang: Spatial Mutli-omics Sequencing the Developing Human Cerebellum
- Session 4
- Alexander van Oudenaarden: Acceleration of Genome Replication Uncovered by Single-cell Nascent DNA Sequencing
- David Weitz: Applications of Single Microbe Sequencing
- Amos Tanay: Single Cell Models for Deciphering the Birth of Cell-type Specific Epigenetics During Gastrulation
- Ge Gao: Rationally Design Generative Models for Delineating the Regulator Map in silico
Oct. 13-14, 2022. Beijng China
Opening
Session 1
Moderator: Xiaoliang Sunney Xie

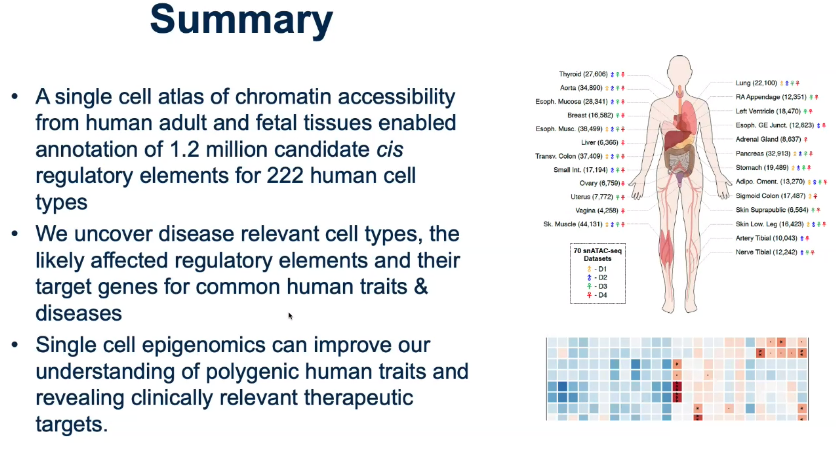
Bing Ren: Illuminating the Dark Matter in Human DNA with Single-cell Epigenomics Analysis
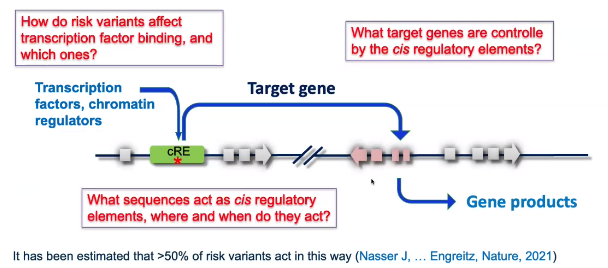
background: “risk variants associated with gene expression regulation”
![image-20221013104254925]()
Method development (sci-based):
Experimental: snATAC-Seq, snMethyl-HiC, Paired-Tag/Seq
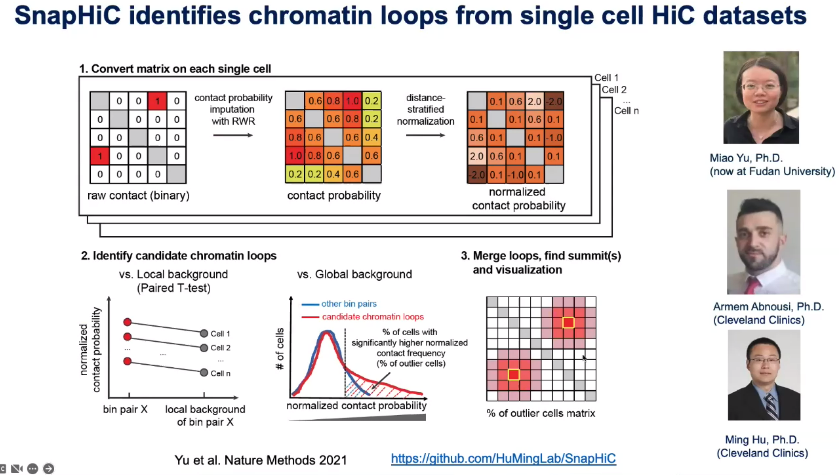
Computational: SnapATAC, SnapHiC
![image-20221013105131216]()
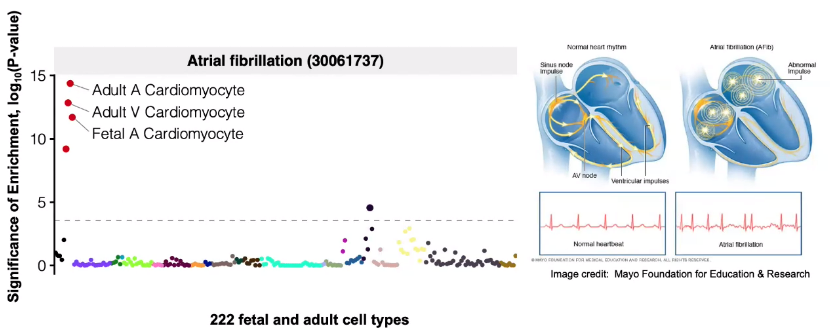
Predicting disease-associated cell types
Utilize GWAS data, analysis enrichment in cell types by intersecting with cCREs.
![image-20221013105850435]()
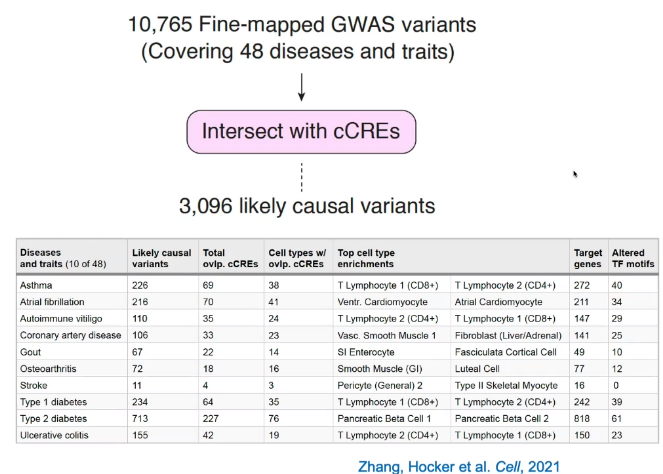
Identify key regulatory elements associated with disease
Summary:
- Q&A:
- Associated cCREs with genes
Jay Shendure: Reconstruction & Recording of Mammalian Development
background: development of single-cell methods
scRNA-seq of ~2 million cells in one experiment (sc-based, $384 ^ 3$ )
![image-20221013112557477]()
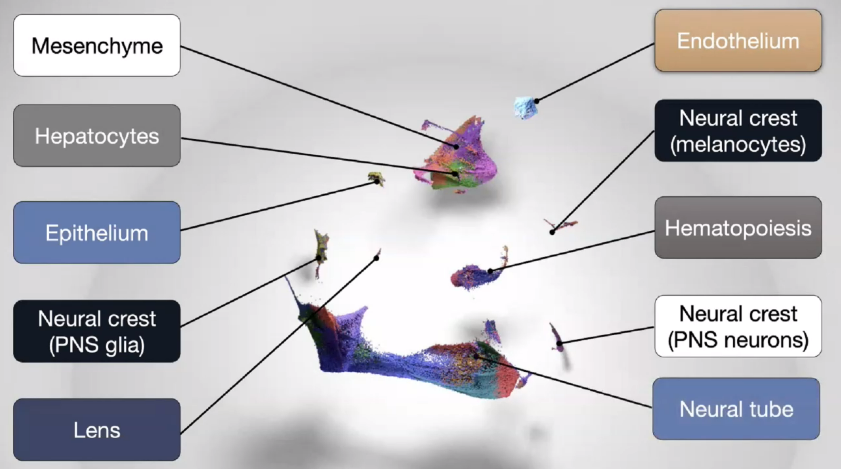
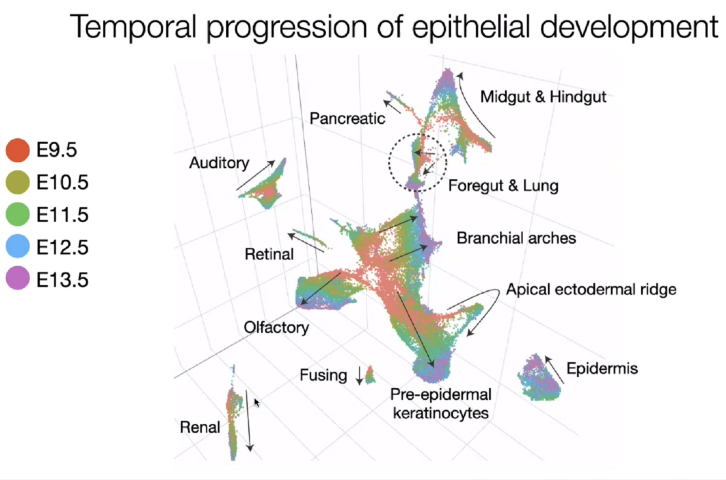
Epithelial development
![image-20221013112701901]()
Session 2
Moderator: Fuchou Tang

Bart Deplancke: Engineering Next-generation Single Cell Phenomics Technologies
DisCo
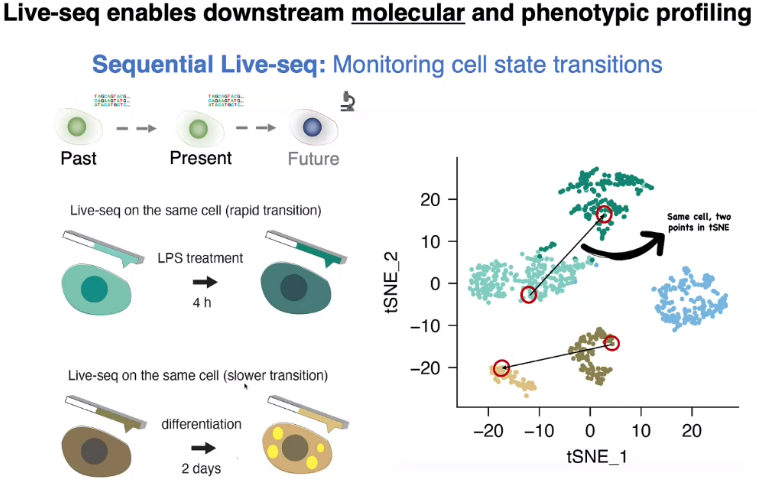
Live-seq
minor perturbation on target cells
sequential Live-seq: state transition of the same cell
![image-20221013155506466]()
transcriptomic recorder
Rickard Sandberg: Scalable Full-length scRNA-seq for Temporal Analyses of Transcription and Dissections of Cell States and Subtypes
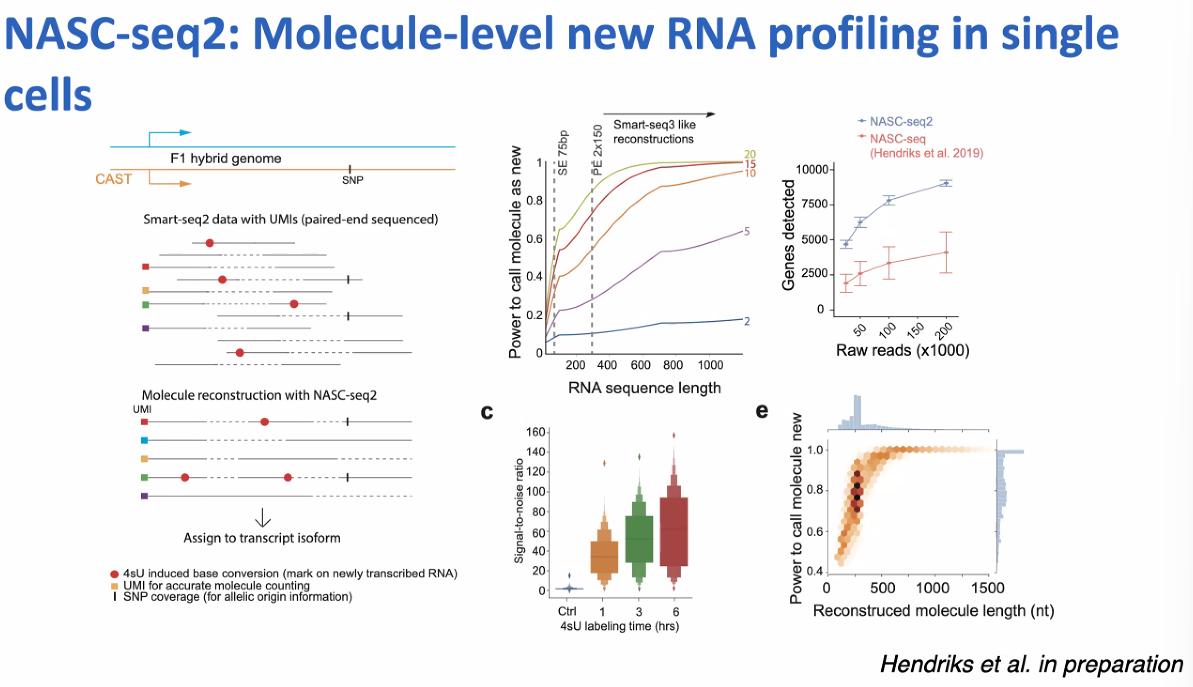
NASC-seq2: single-cell nascent RNA sequencing
![image-20221013161723120]()
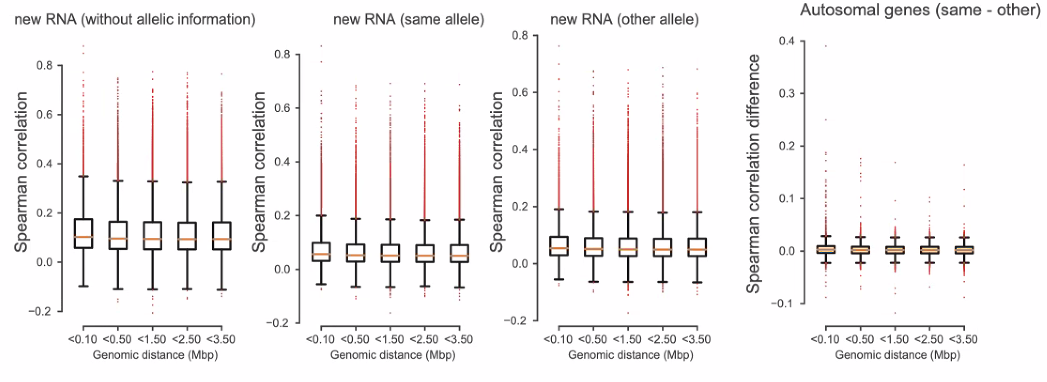
Co-bursting: do nearby genes burst independently?
![image-20221013162052659]()
general independent transcription of two alleles
![image-20221013162407531]()
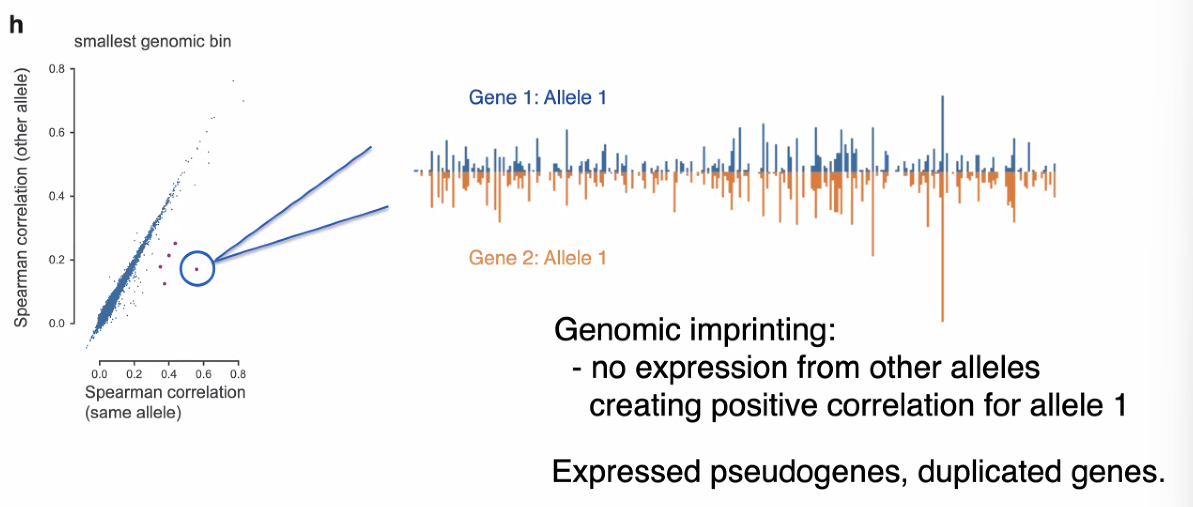
co-bursting outliers :
![image-20221013162527330]()
Smart-seq3xpress: scalable, cost efficient
questions:
pseudo-gene expression and duplicated genes may contributed to co-bursting outliers. mentioned pseudo-gene expression. however, the investigation of pseduo-gene influenced by the high sequence similarity, specific steps to resolve this.
Angela Ruohao Wu: Multi-step Single-cell Multi-omics Methods for Simultaneous Dissection of Phenotype and Genotype Heterogeneity from Frozen Tumors
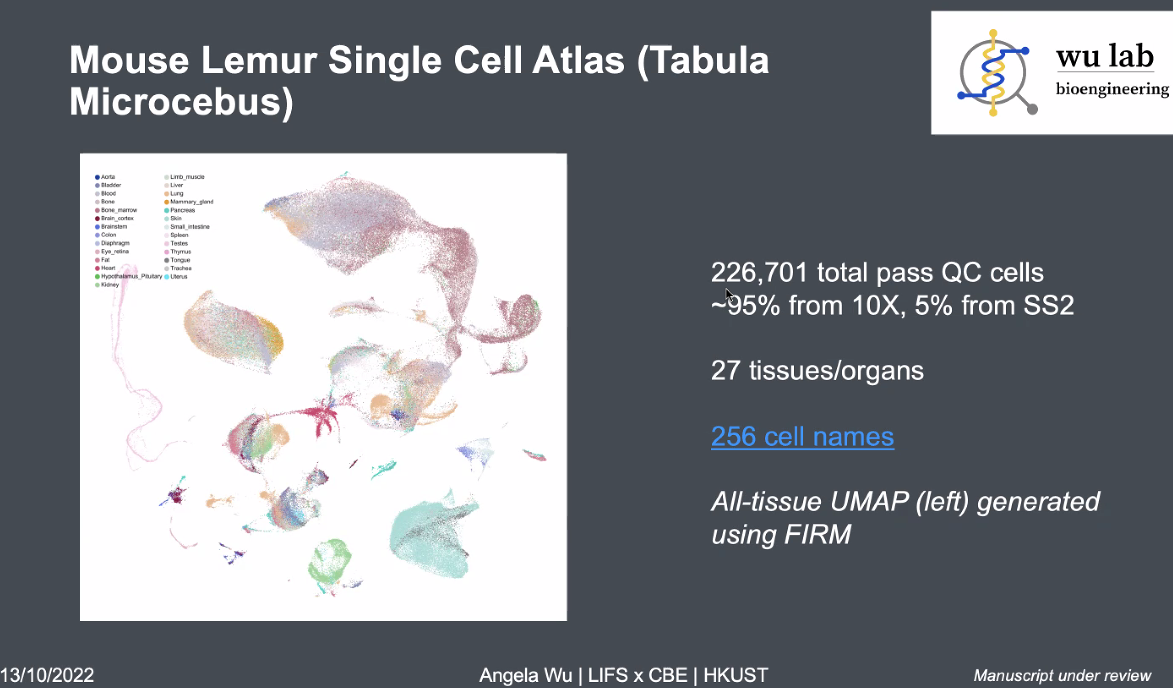
Mouse Lemur Single Cell Atlas
![image-20221013164210589]()
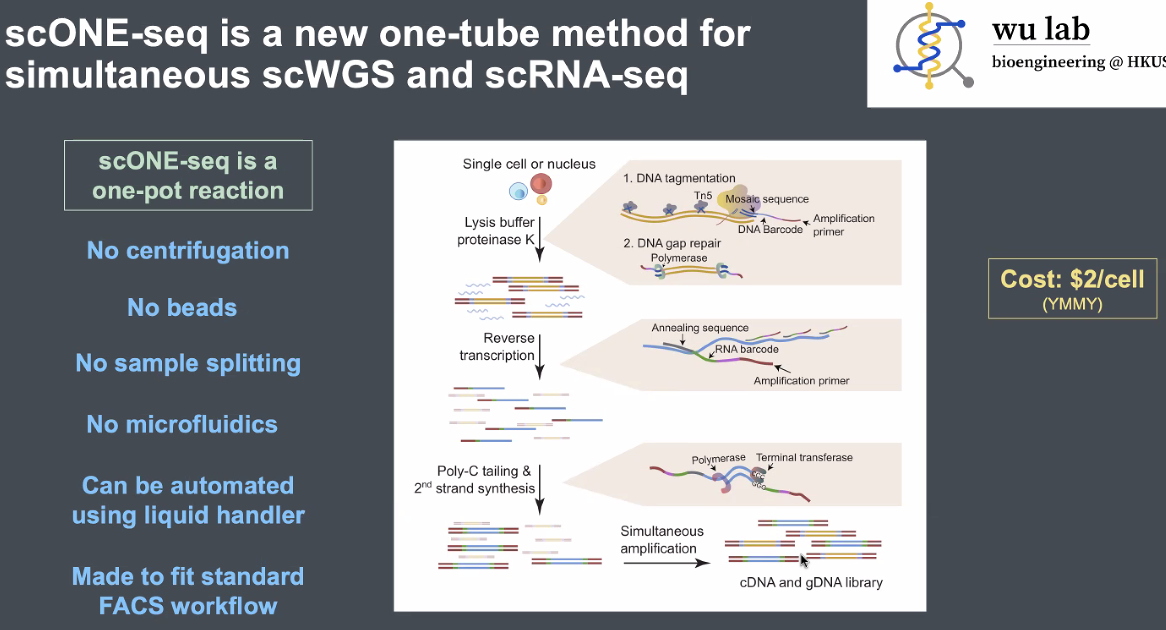
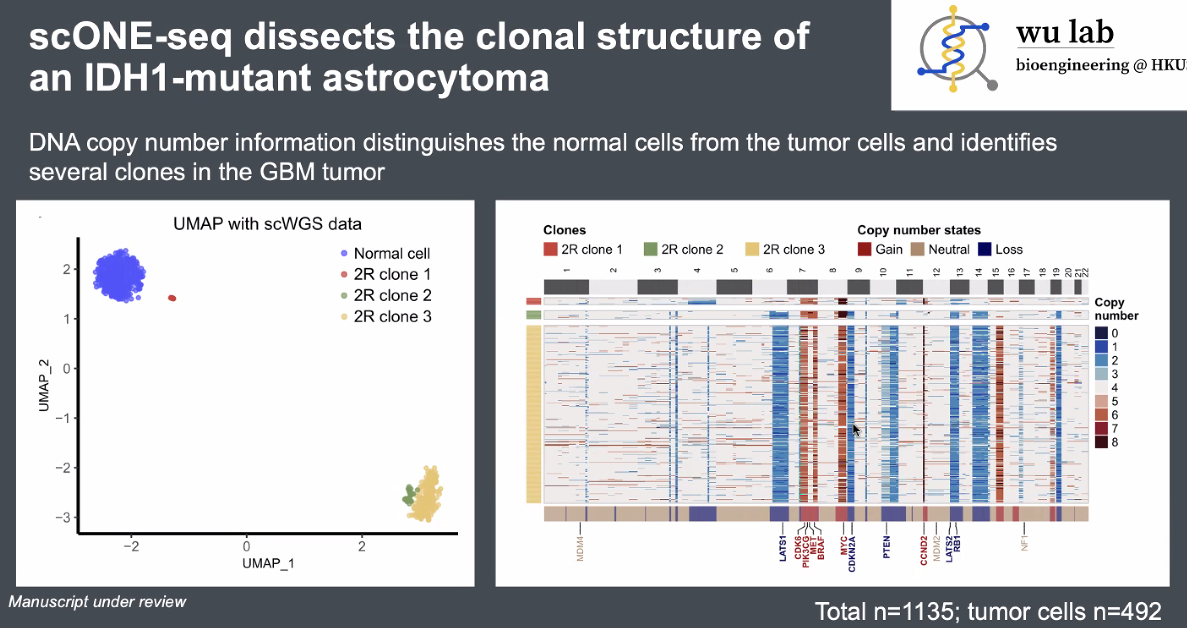
scONE-seq: one tube single-cell WGS and RNA-sequeicing
single-cell multi-omics is especially useful for cancer analysis.
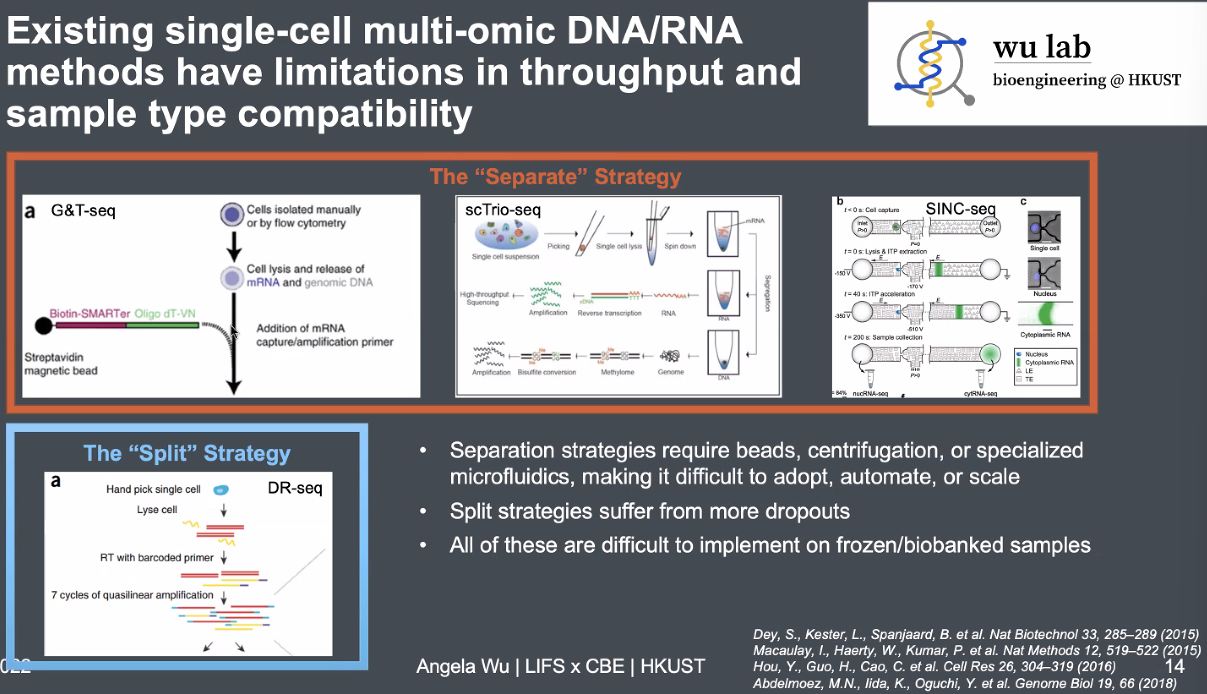
existing single-cell DNA&RNA methods:
![image-20221013164720689]()
principles of scONE-seq
![image-20221013164806662]()
performance:
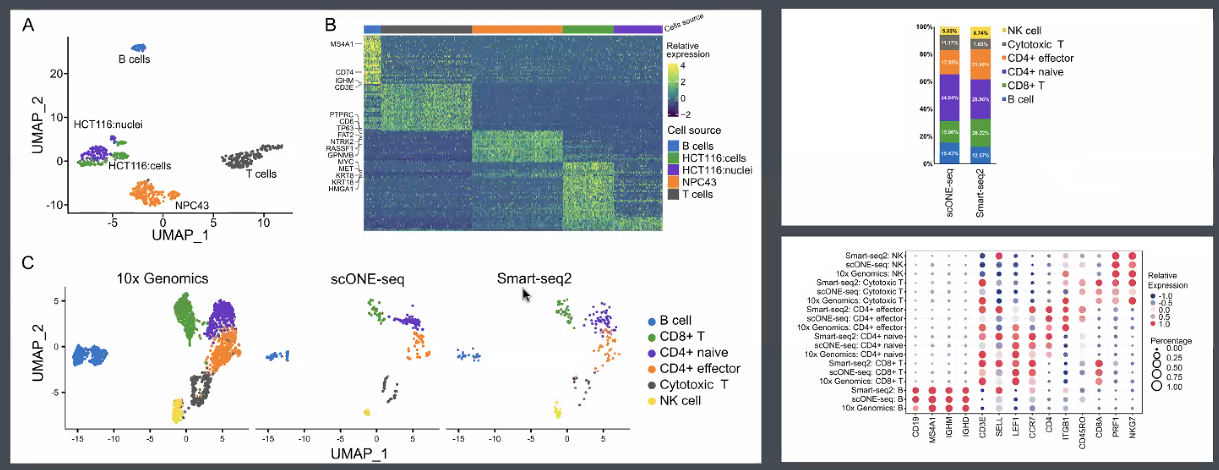
RNA (total RNA):
![image-20221013164937465]()
CNV:
![image-20221013165115827]()
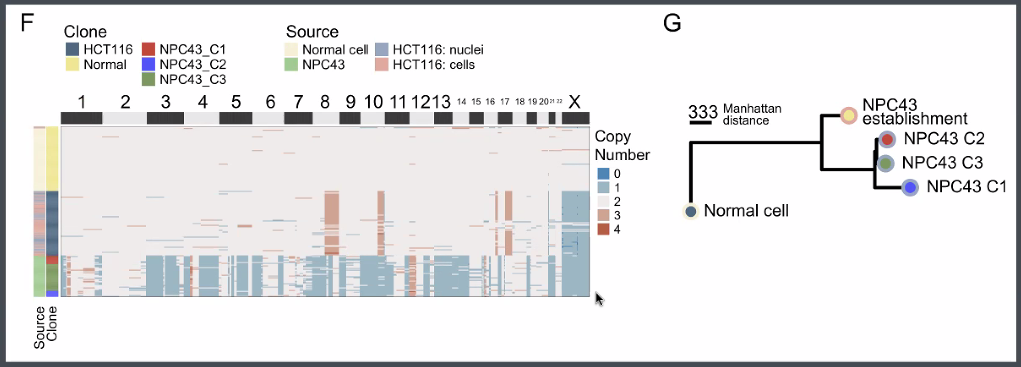
discoveries:
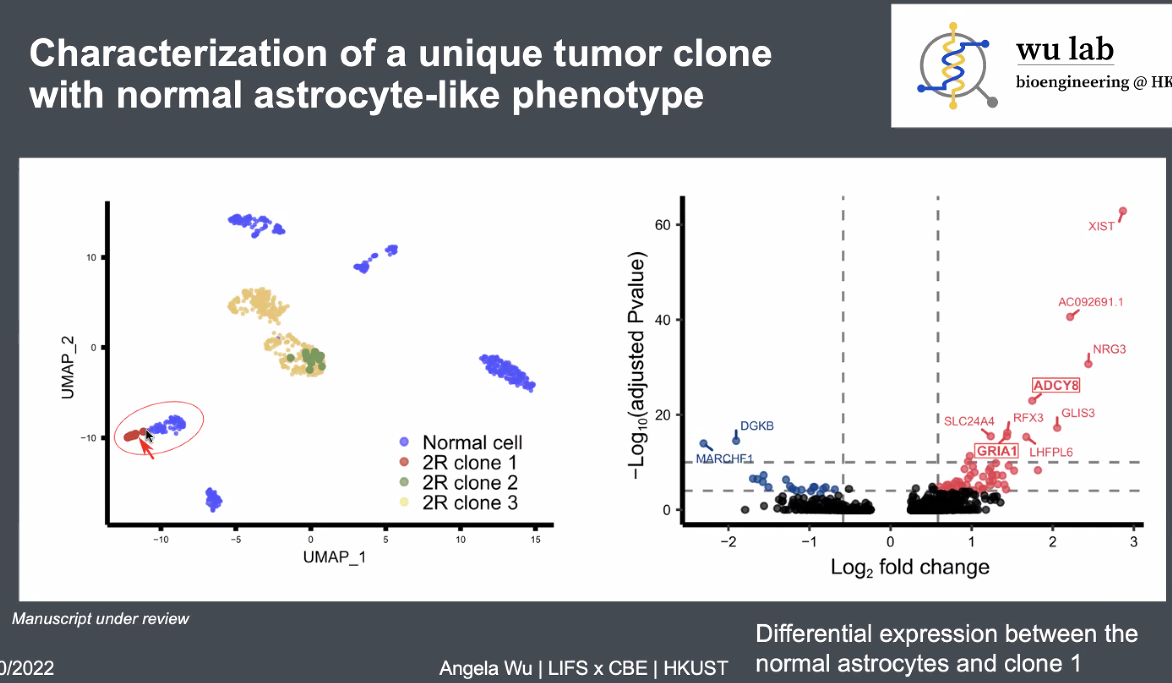
a novel tumor sub-clone in astrocytoma
![image-20221013165506031]()
Tumor cells with minor difference on transcription identified from CNV information,
![image-20221013165838767]()
summary
![image-20221013170129976]()
Guoji Guo:Mapping Cell Landscapes at Single cell Level
background: equation for cell fate decision
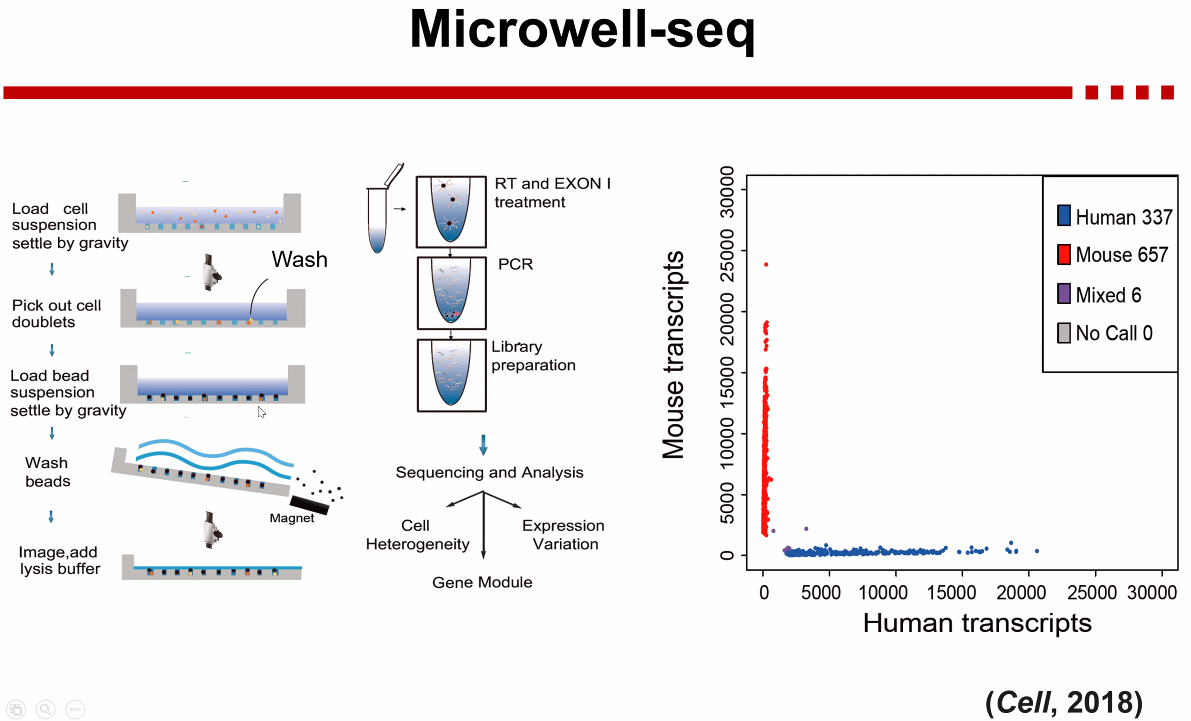
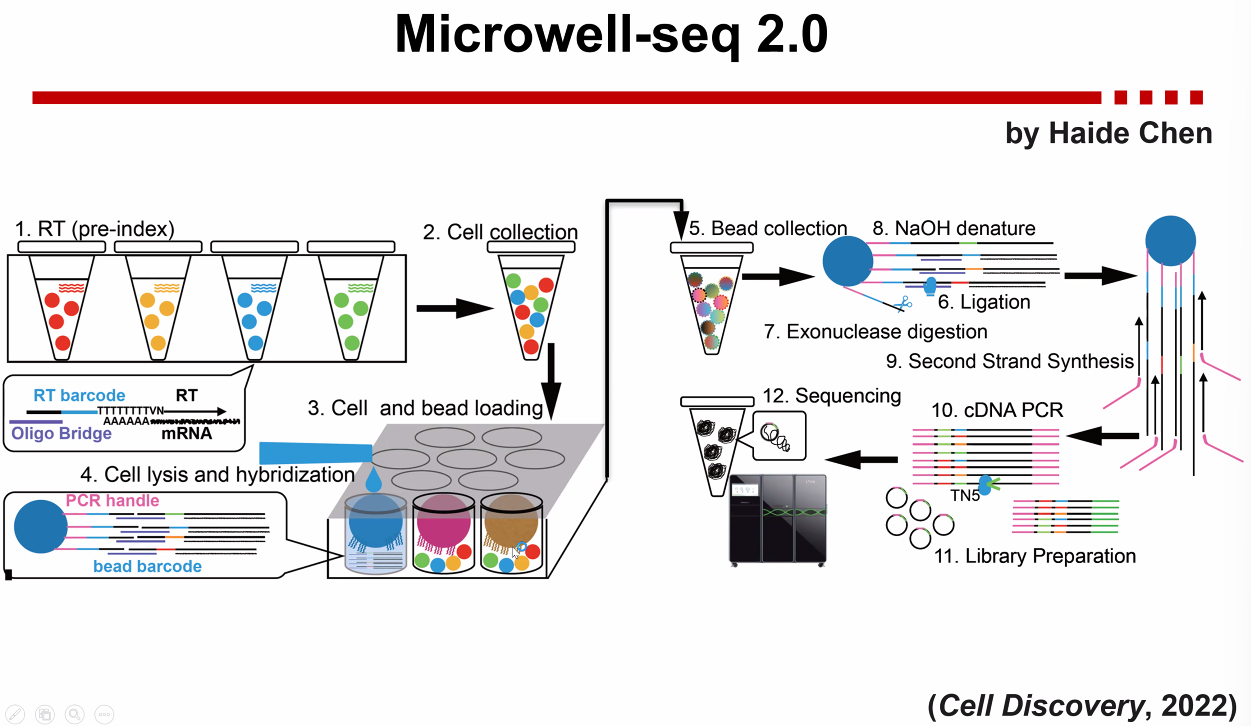
Microwell-seq
![image-20221013171252054]()
Microwell-seq 2.0
![image-20221013171408431]()
- human atlas
- inflamed structural (endothelial, epithelial, stromal) cells, validated in vivo.
mouse atlas
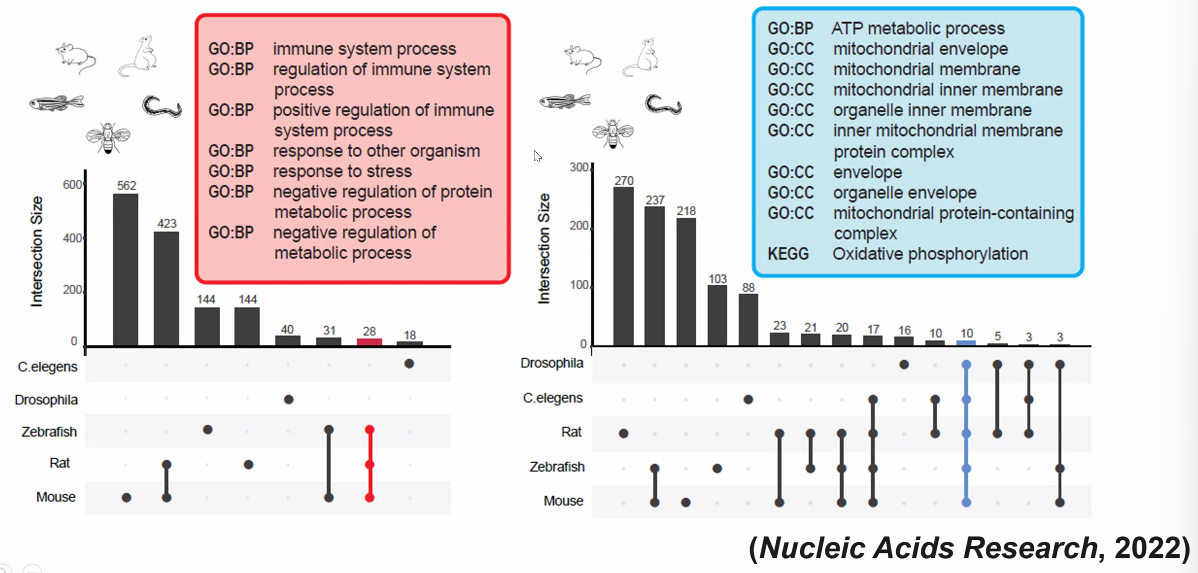
lifespan cell landscape analysis
![image-20221013171855788]()
- inflammation in structural cells
- mitochondria metabolism
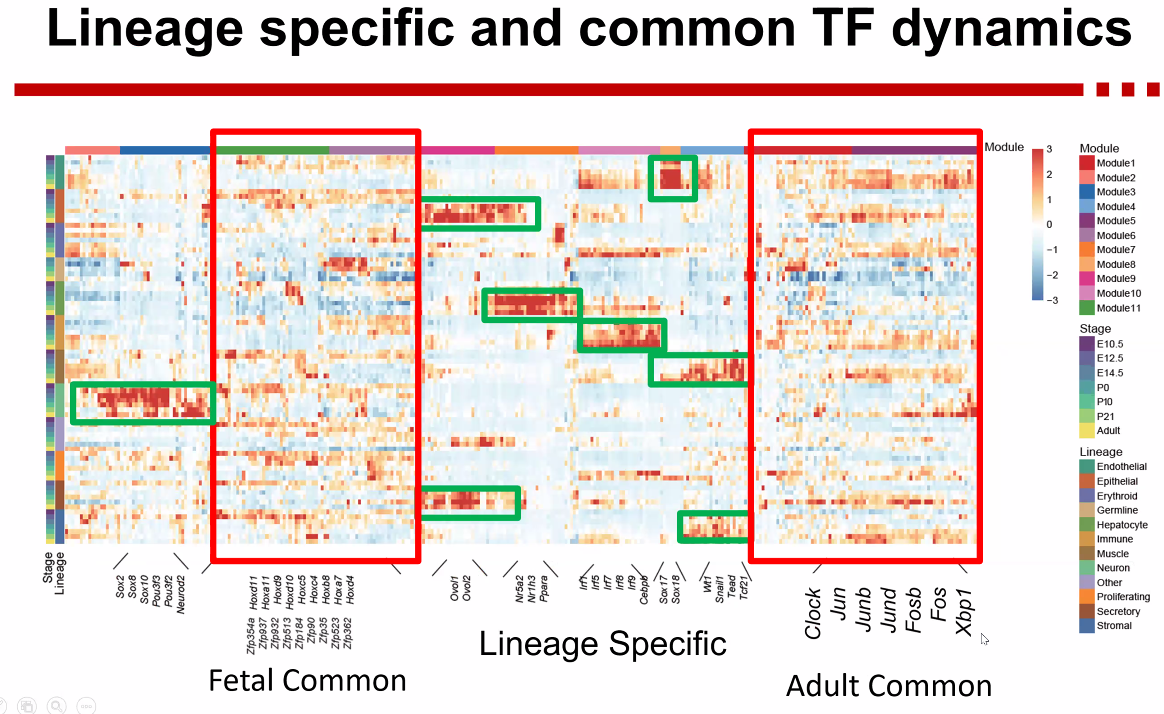
how cell types are regulated?
- TF dynamics
![image-20221013172440815]()
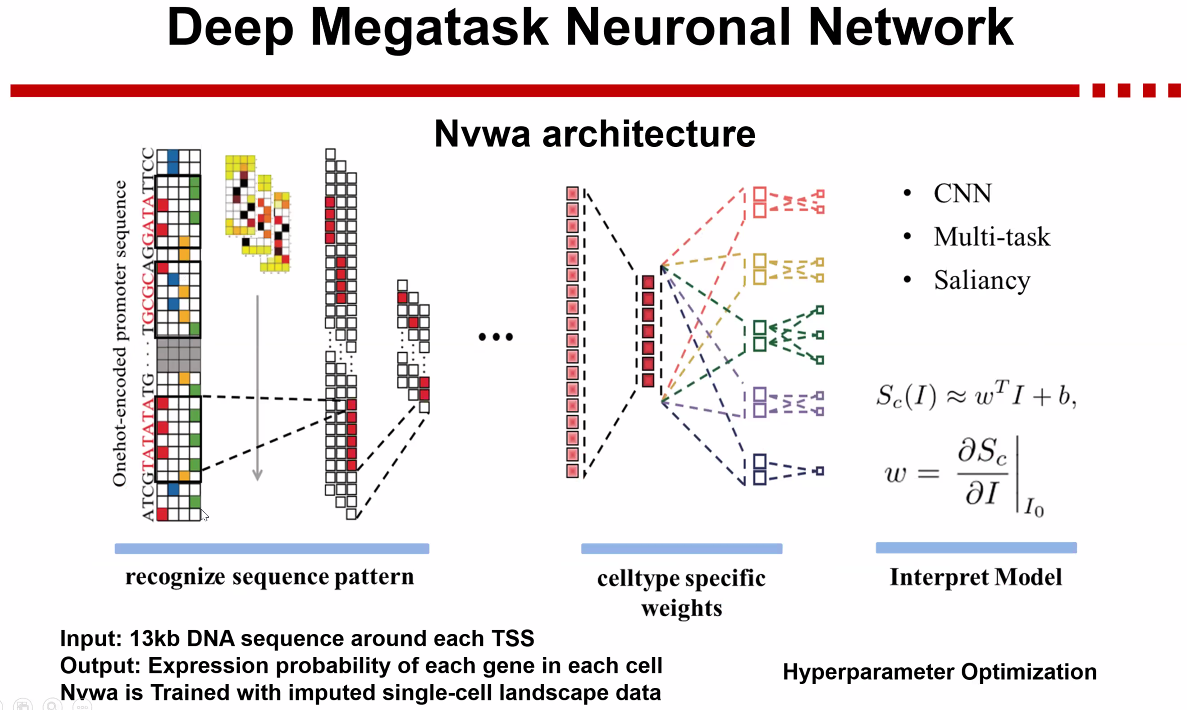
- Cross-species analysis of common TFs during differentiation
Nvwa
![image-20221013172827826]()
Chenghang Zong: Total-RNA Based scRNA-seq Allows Genome-wide Identification of Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Regulation
background: Total-RNA based single-cell RNA-seq
![image-20221013174643712]()
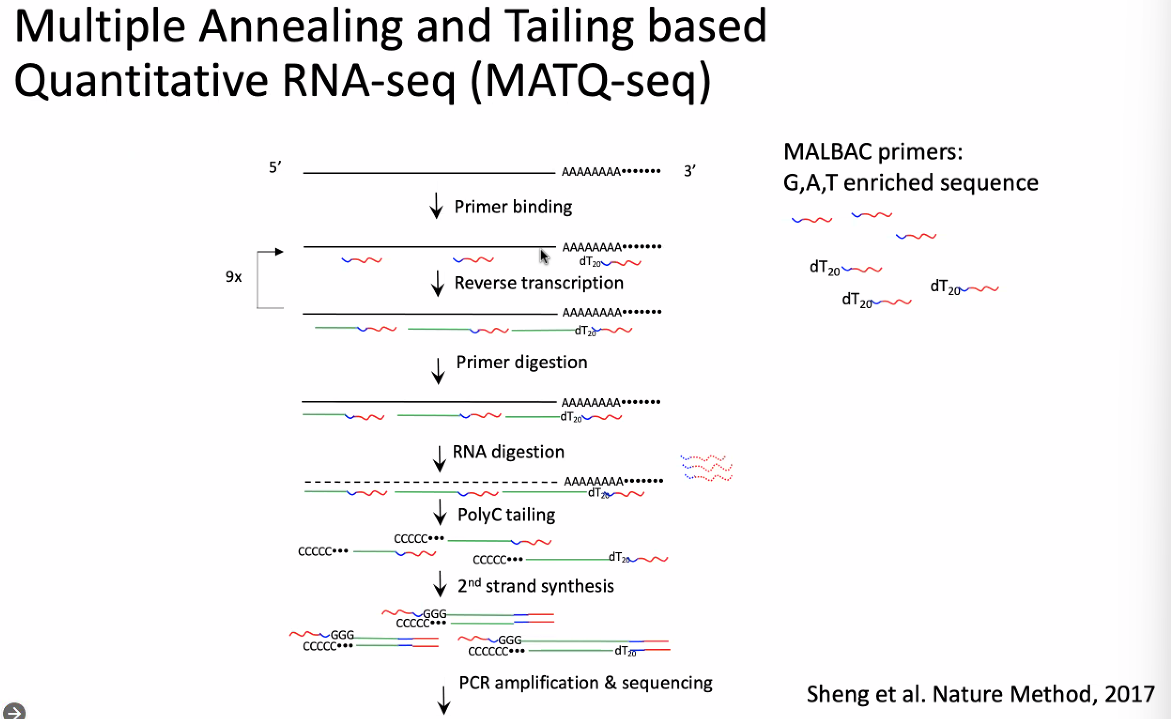
chemistry of MATQ-seq:
![image-20221013174751062]()
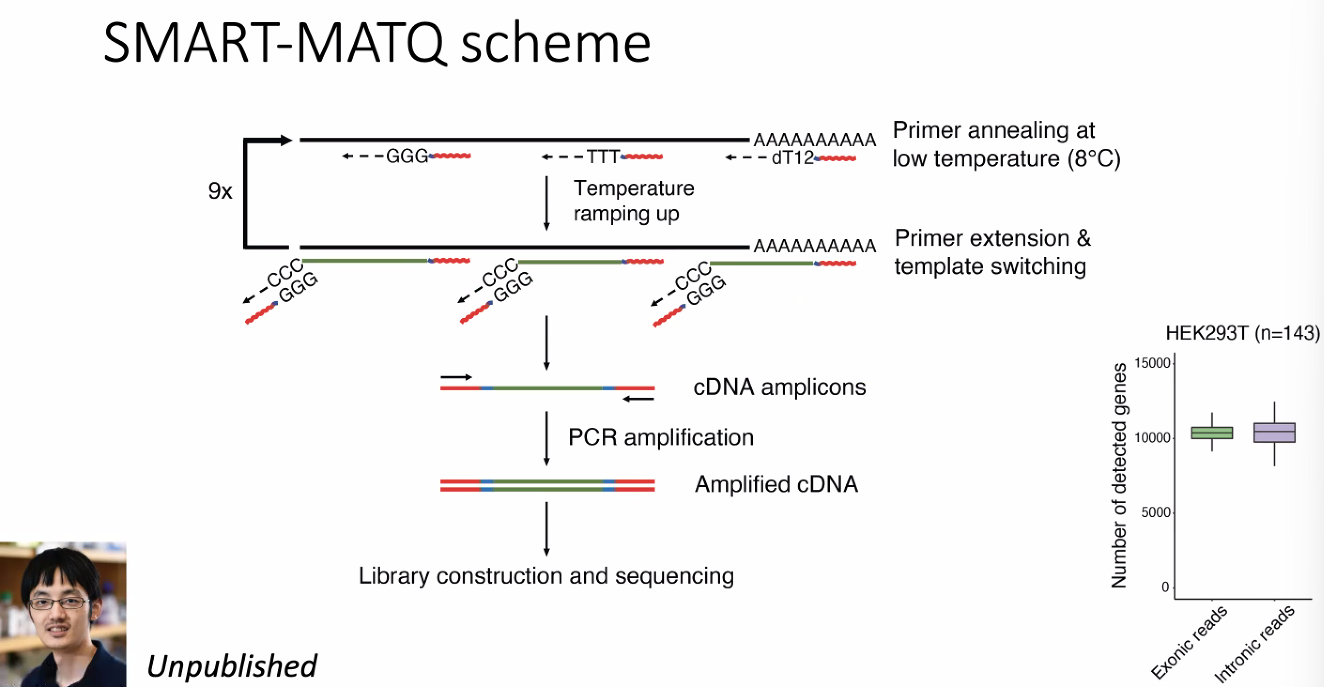
SMART-MATQ seq
![image-20221013174909036]()
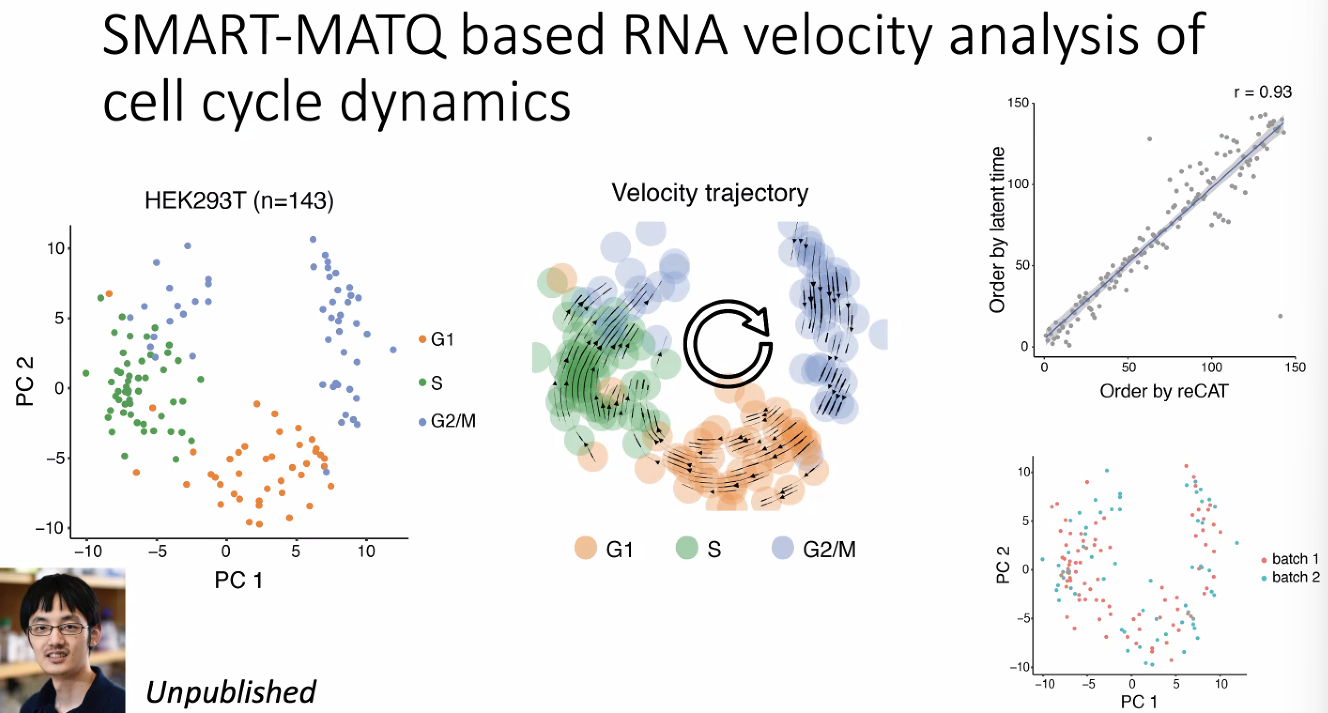
include intron (nascent), more appropriate for RNA velocity.
characterize the cell dynamics in cell cycle
![image-20221013175307403]()
differential gene expression along certain trajectory:
method: tradeSeq (2020, Nat commu)
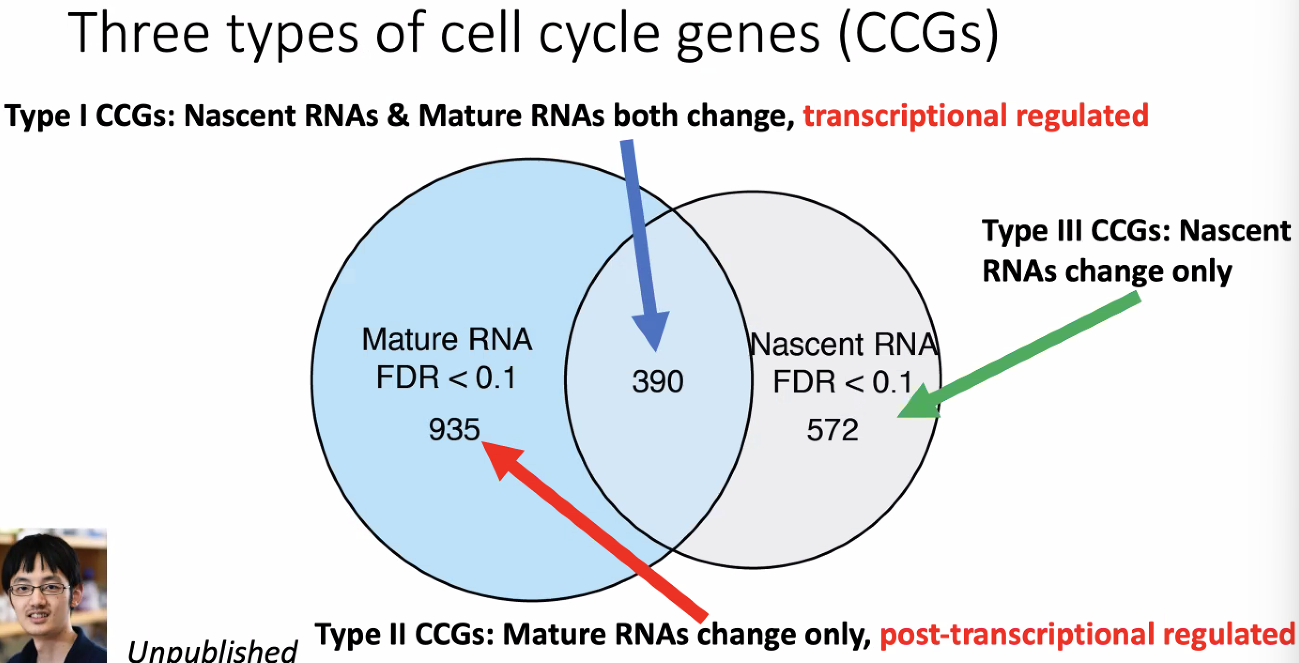
compare DEG of mature and nascent RNAs defines 3 types of distinct cell cycle genes (CCGs)
![image-20221013175527200]()
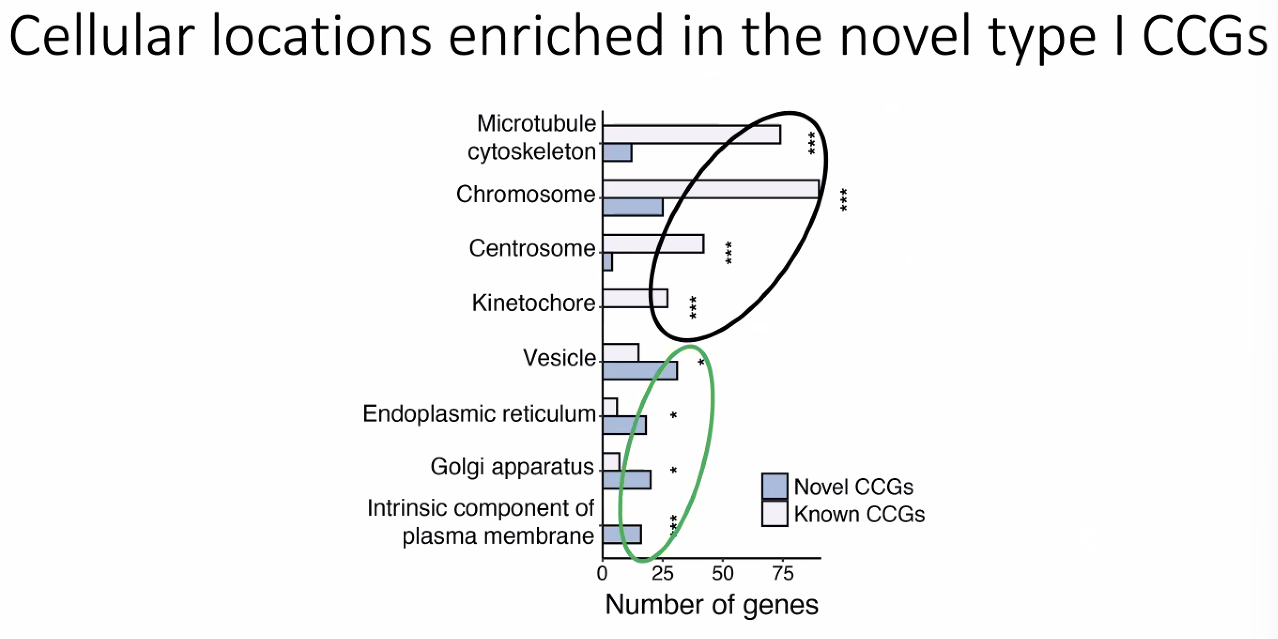
Novel cell cycle genes
![image-20221013175908999]()
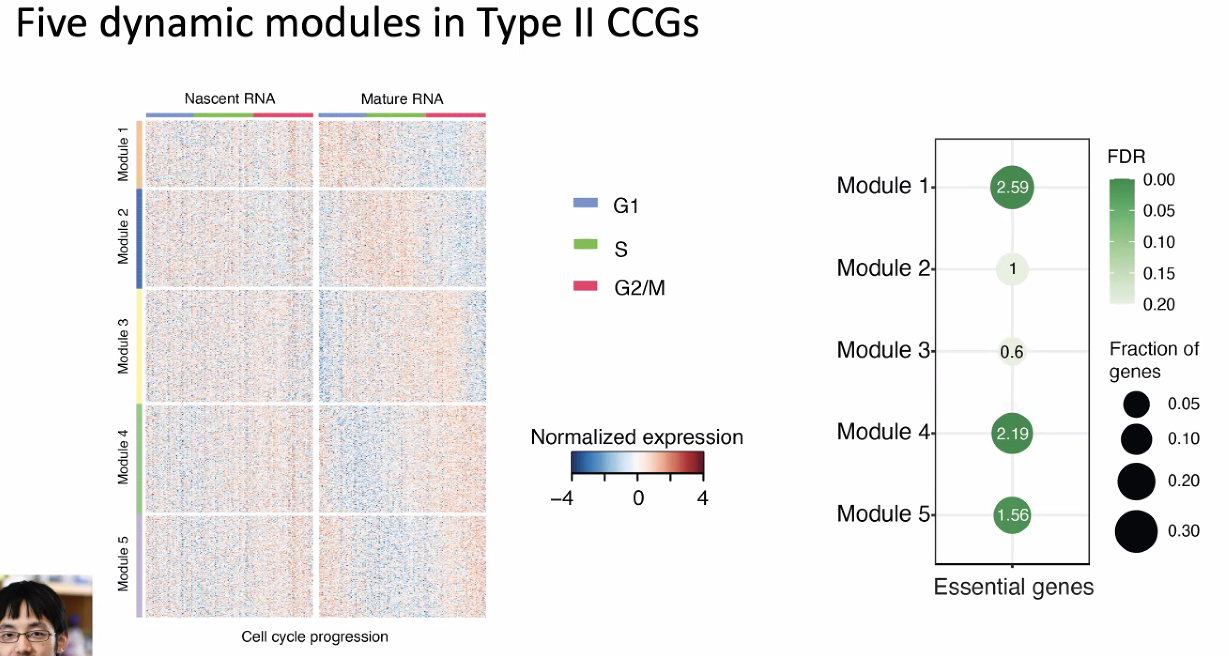
dynamic modules in different CCGs
![image-20221013180053256]()
Question:
- during CCG identification, the significance of type III CCGs? (nascent only) how to explain stochastic fluctuation or some biological mechanisms.
- why identify novel CCGs in type I? since type 1 could be detected by mature RNA alone.
附赠一个彩蛋hhhh
Section 3
Moderator: Yanyi Huang

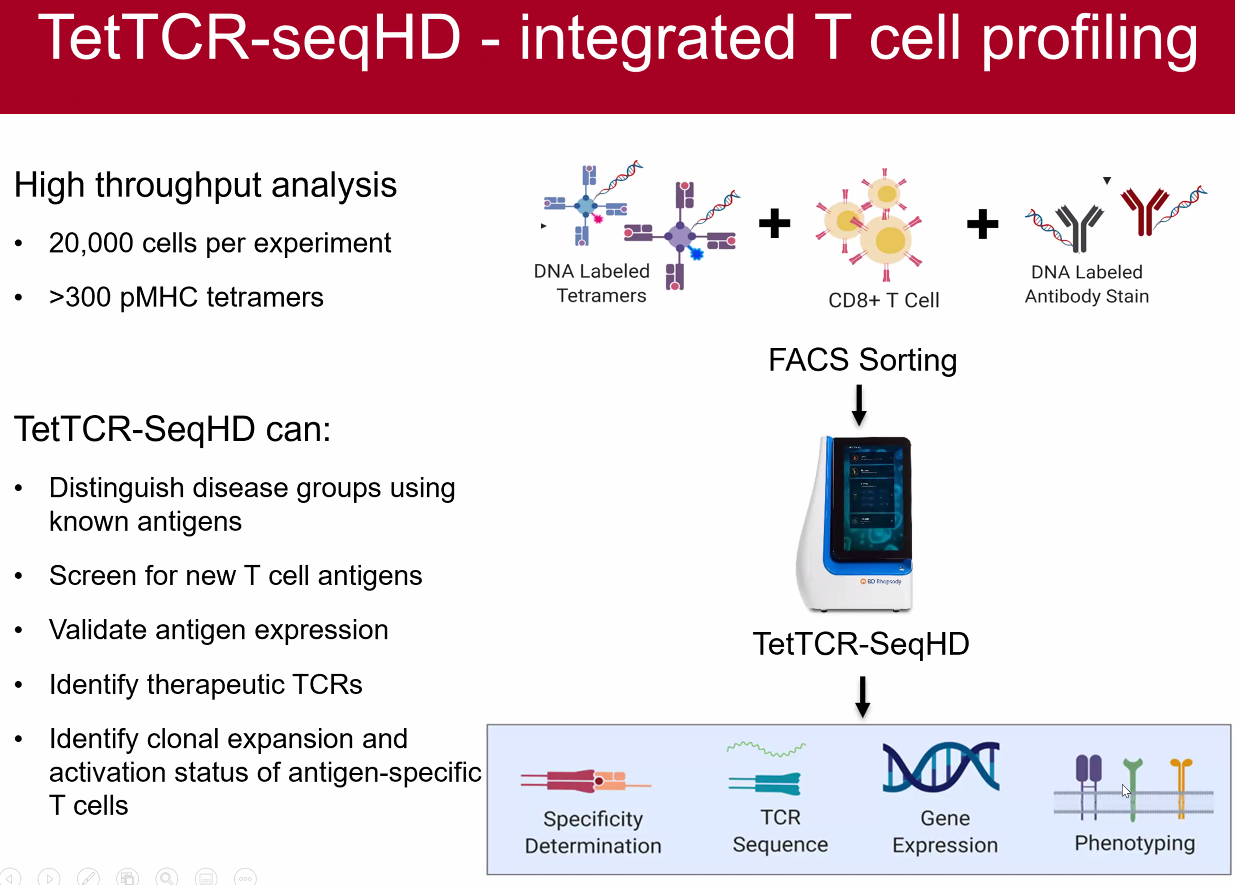
Ning Jenny Jiang: High-throughput and High-Dimensional Single T Cell Profiling
pMHC generation by IVTT
TetTCF-seqHD
![image-20221014095053647]()
performance on CD8+ T cells
conclusions
![image-20221014100035359]()
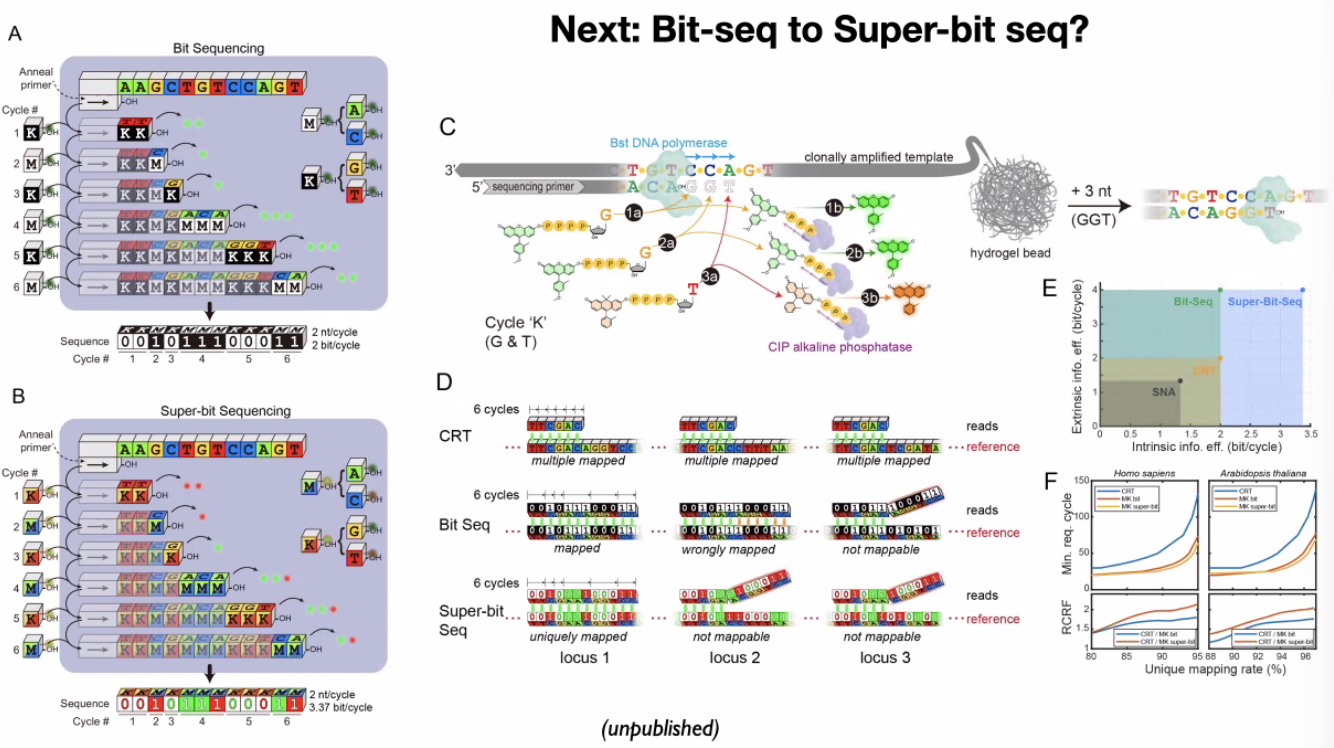
Yanyi Huang: Improving the Information Efficiency for Fast and Spatially Resolved Sequencing
ECC sequencing methods:
bit-seq
![image-20221014102317219]()
Fuchou Tang: Single Cell Omics Sequencing Technologies: The Next Generation
- SCAN-seq: full-length scRNA-Seq
- SCAN-seq2: higher throughput
- SMOOTH-seq2: scWGS sequencing
- single-cell assembly
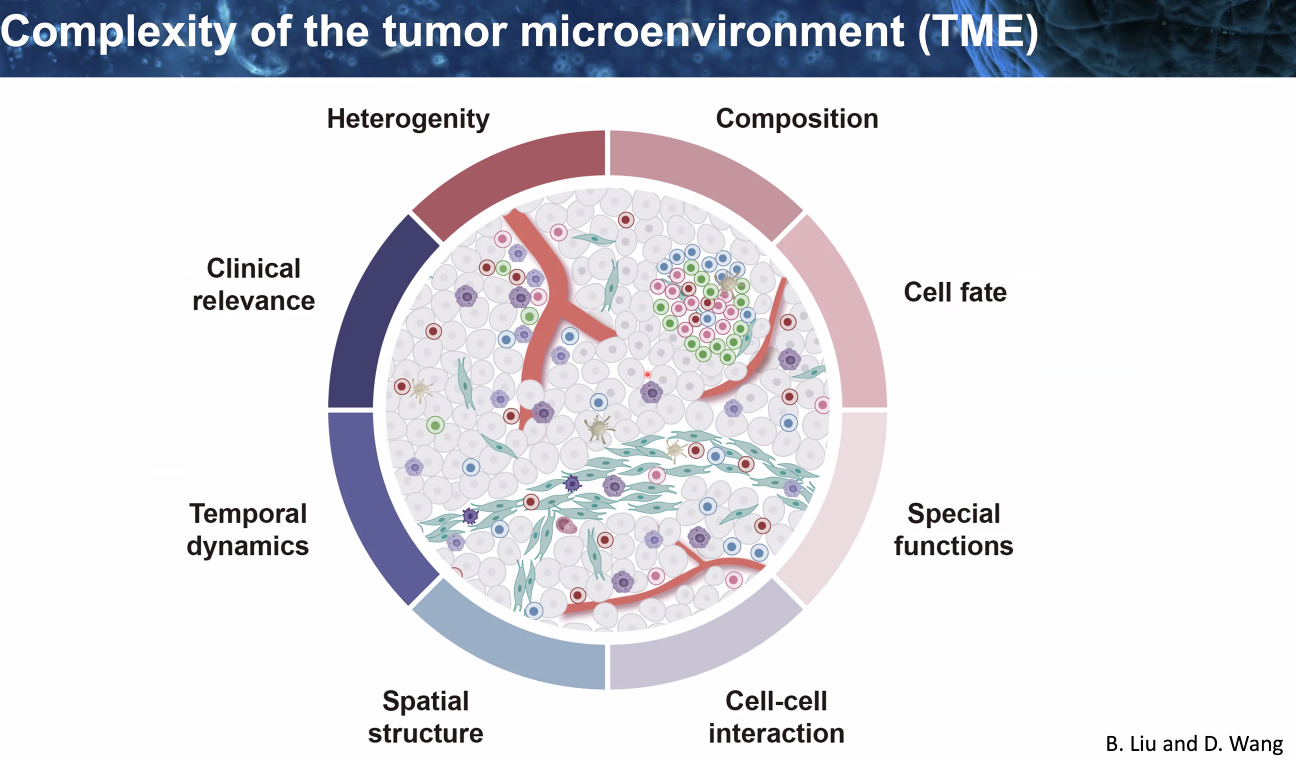
Zemin Zhang: Dynamic Changes of The Tumor Micro-environment During Immunotherapies
background: tumor microenvironmnt
![image-20221014111325598]()
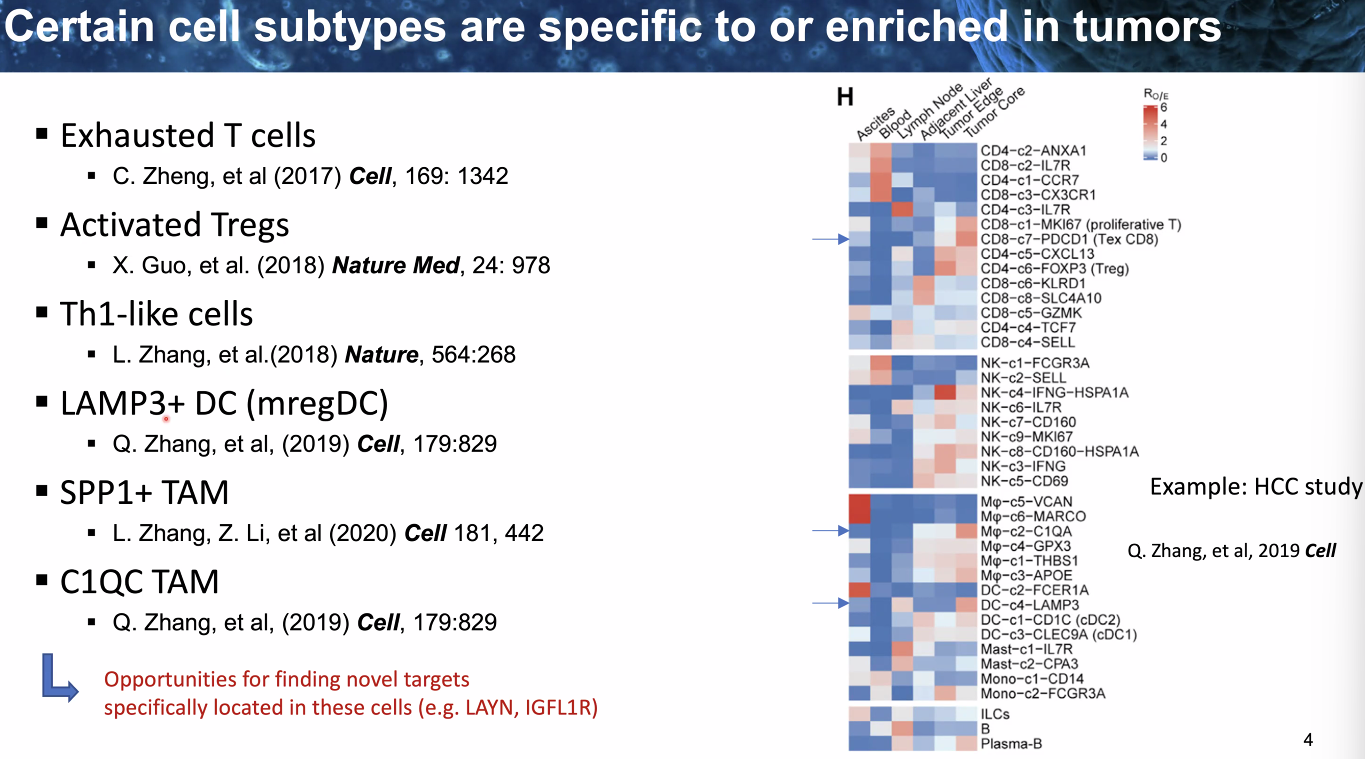
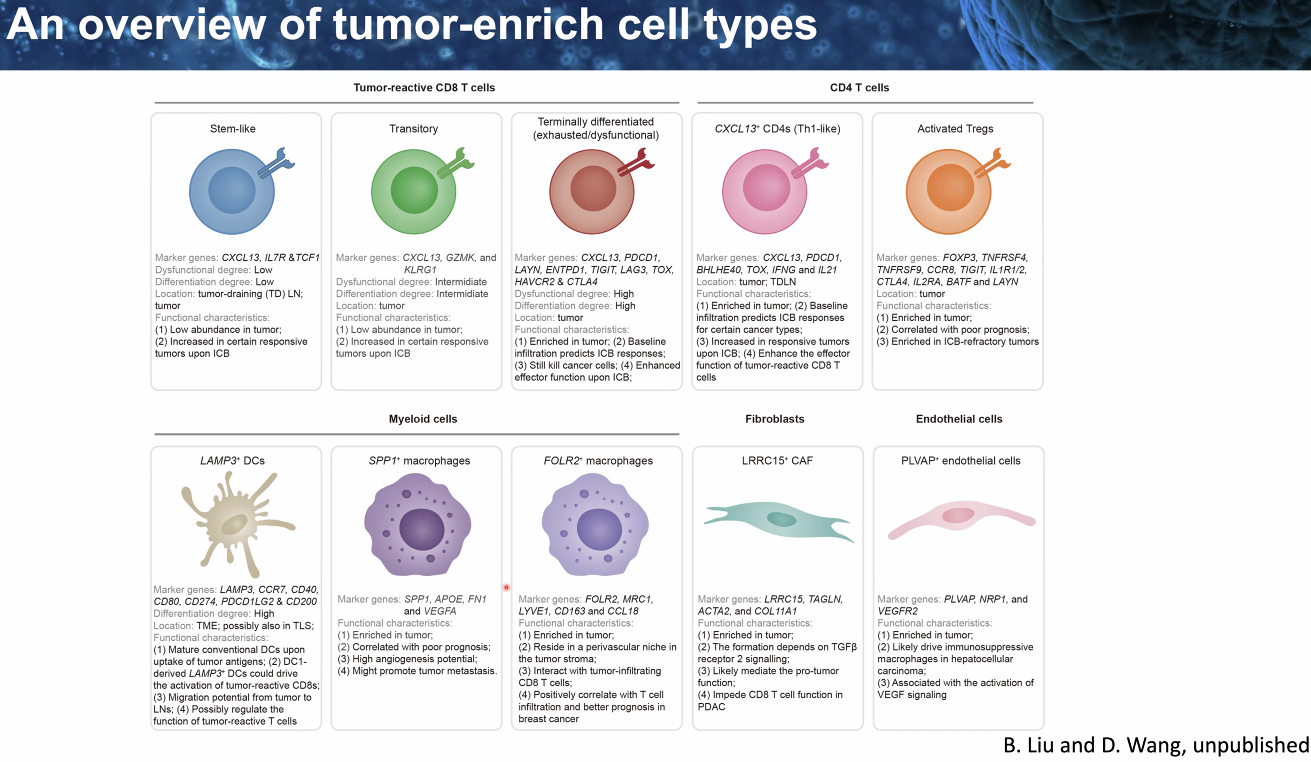
composition: certain cell types
![image-20221014111458791]()
![image-20221014111600587]()
heterogenity:
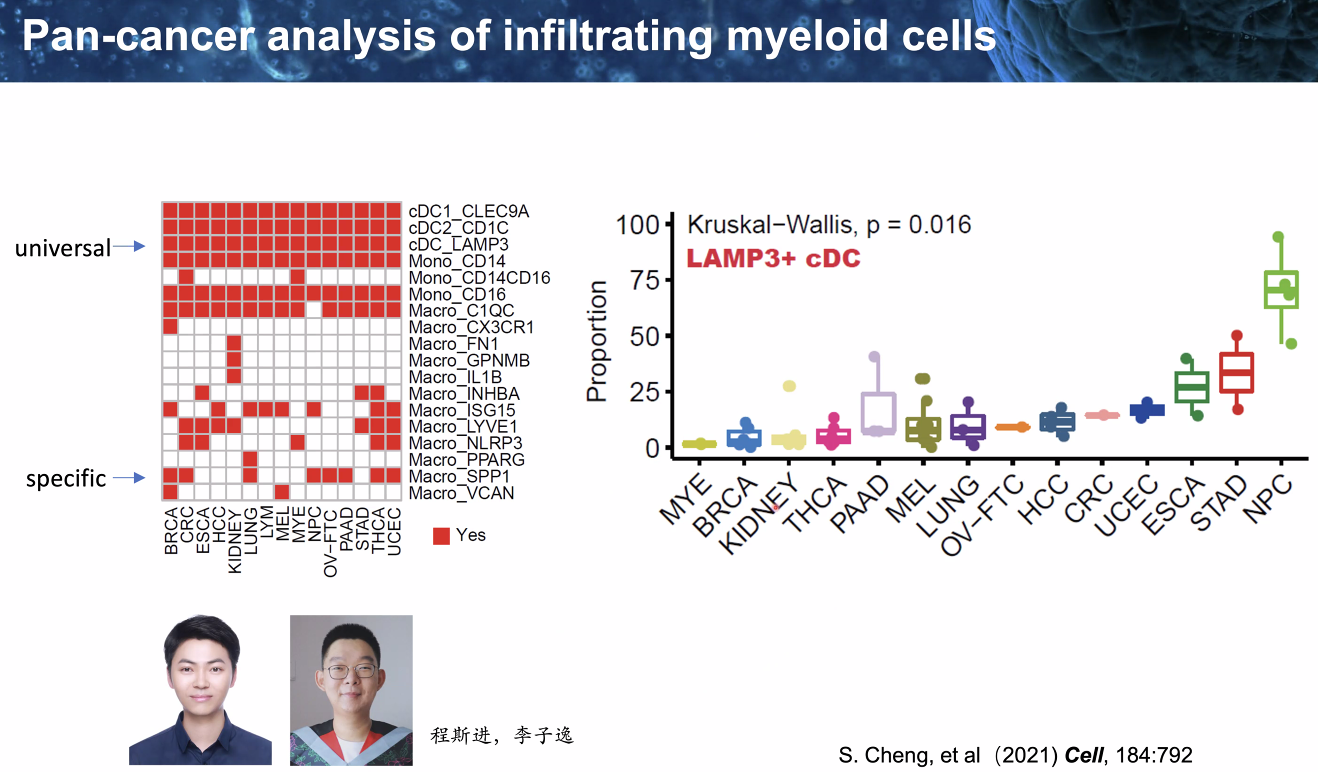
pan-cancer analysis of infiltrating myeloid cells
![image-20221014111735356]()
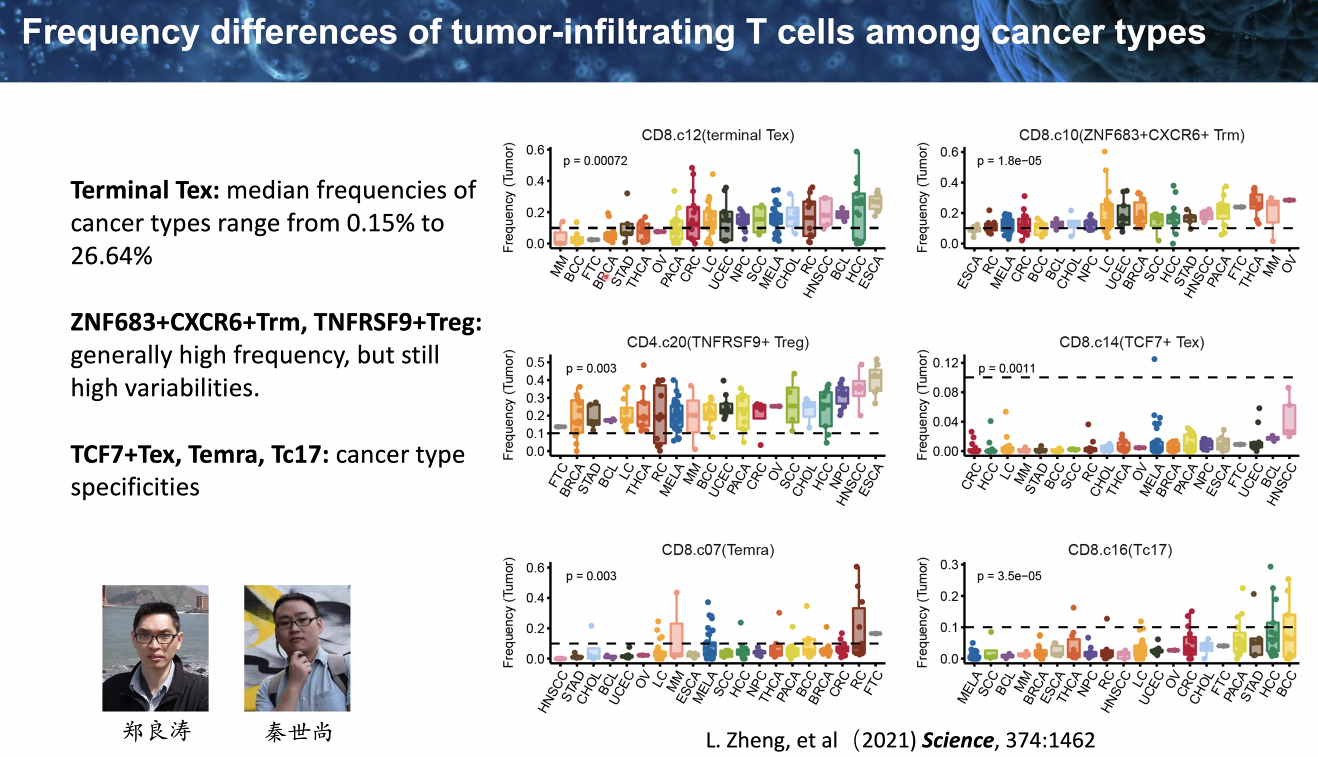
pan-cancer analysis of infiltrating T cells
![image-20221014111810332]()
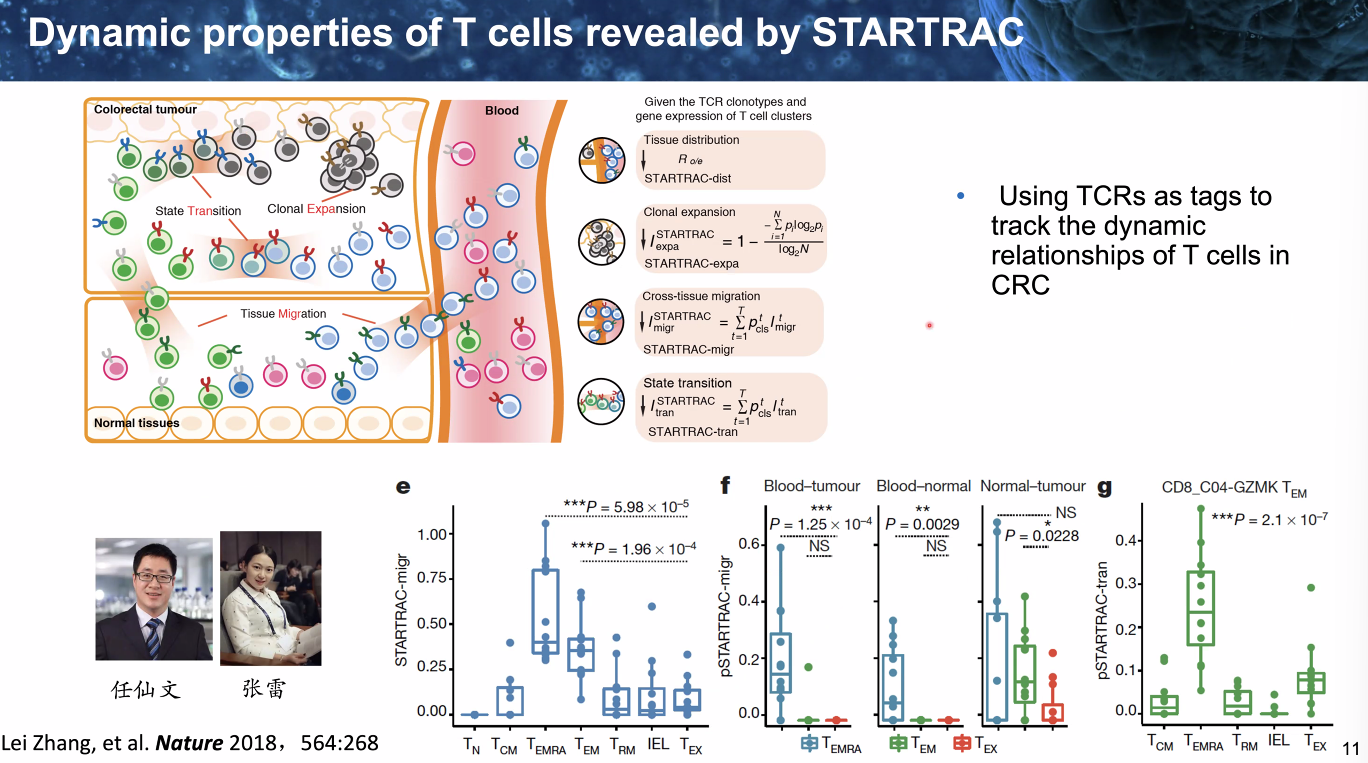
Temporal dynamics
dynamics of T cells
![image-20221014111847298]()
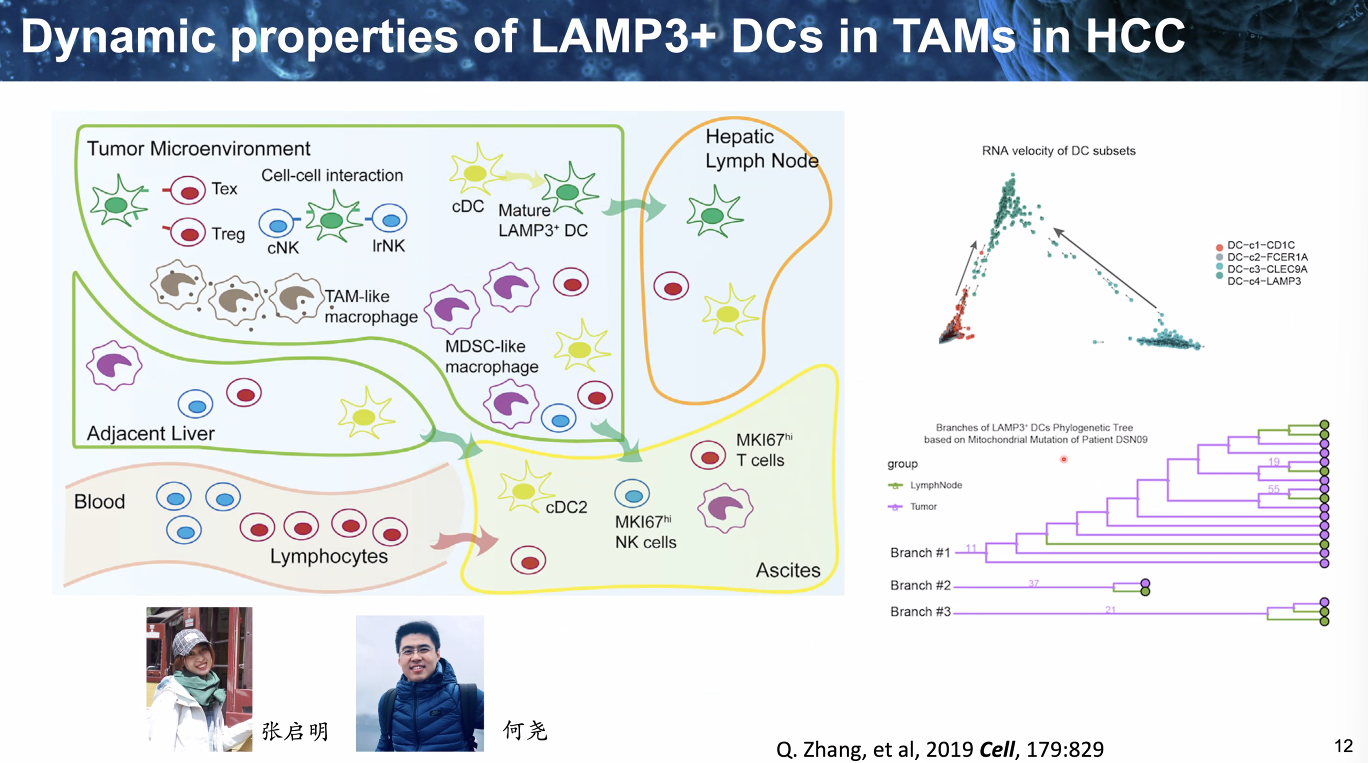
dynamics of LAMP3+ DCs in TAMs in HCC
![image-20221014111920663]()
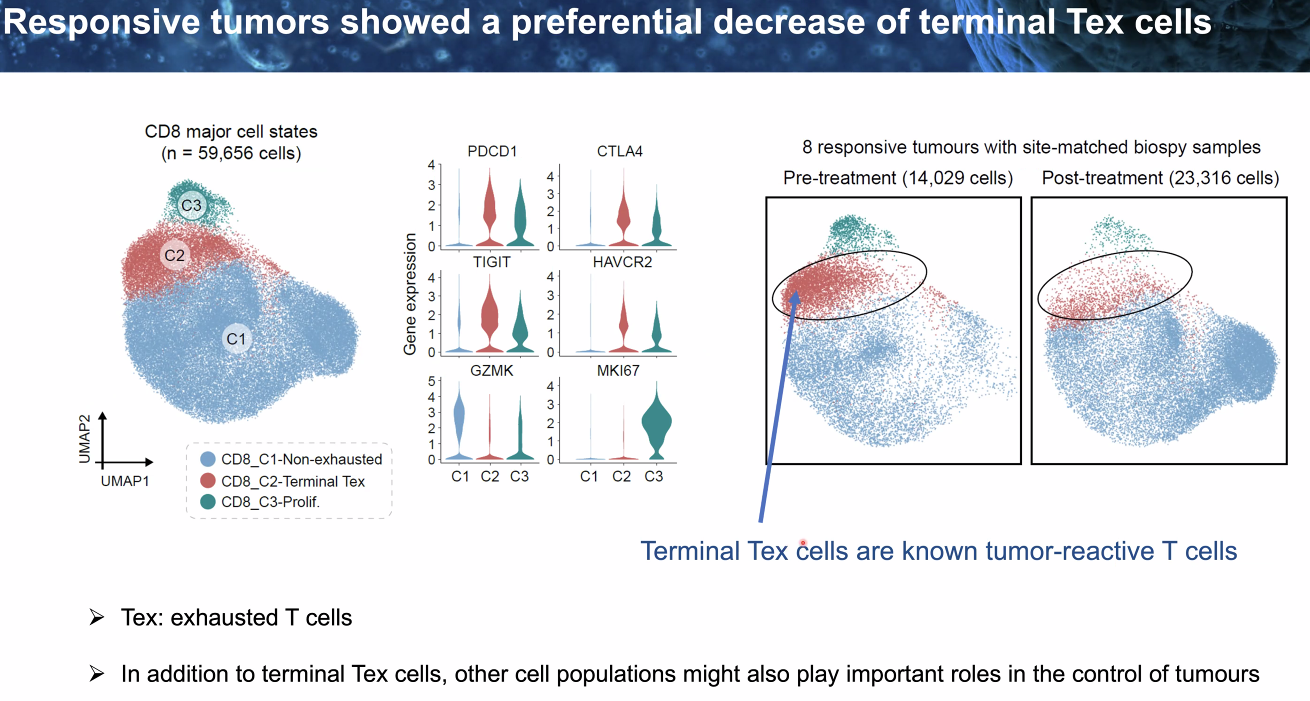
clinical relavance
responsive tumor showed decrease of terminal Tex
![image-20221014112136958]()
Xiaoqun Wang: Spatial Mutli-omics Sequencing the Developing Human Cerebellum
Session 4
Moderator: Yanyi Huang

Alexander van Oudenaarden: Acceleration of Genome Replication Uncovered by Single-cell Nascent DNA Sequencing
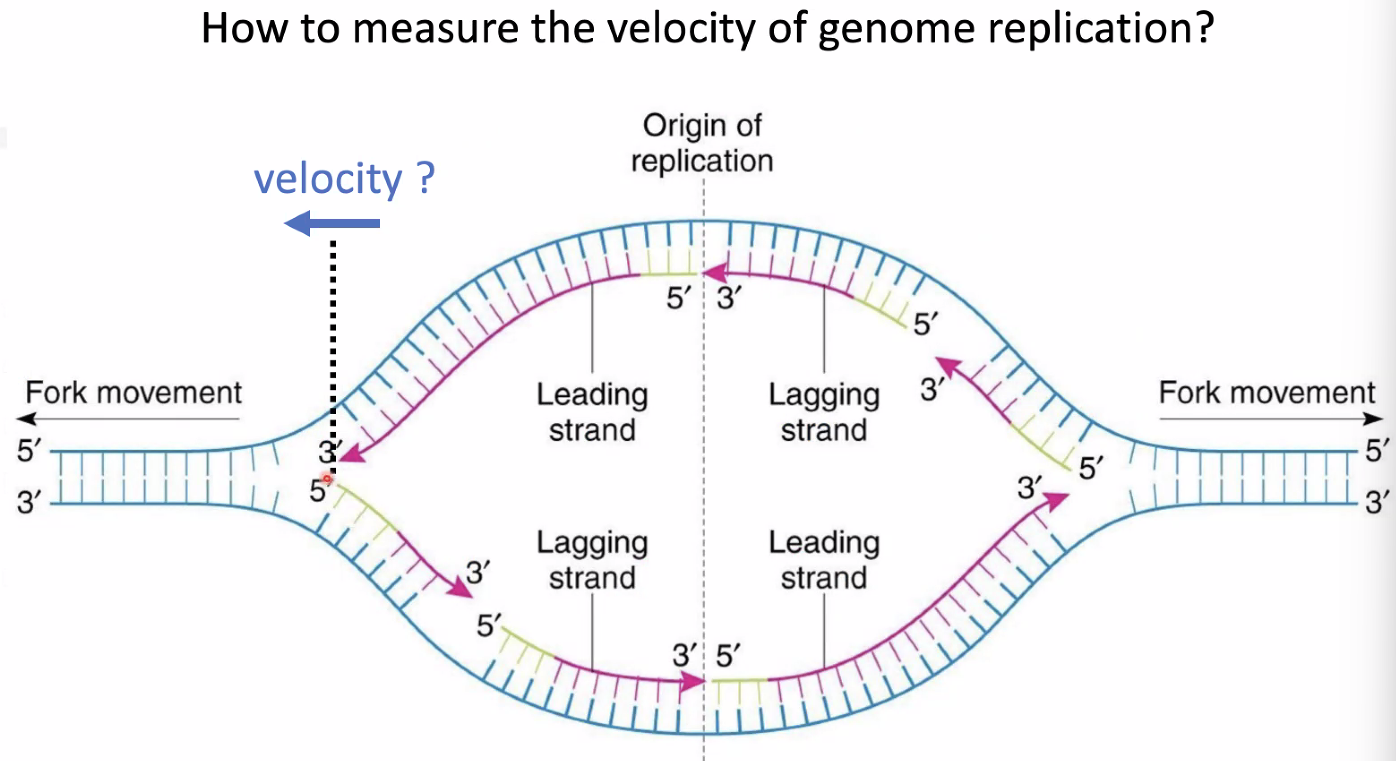
question: measure velocity of genome replication
![image-20221014153223277]()
single-molecule methods
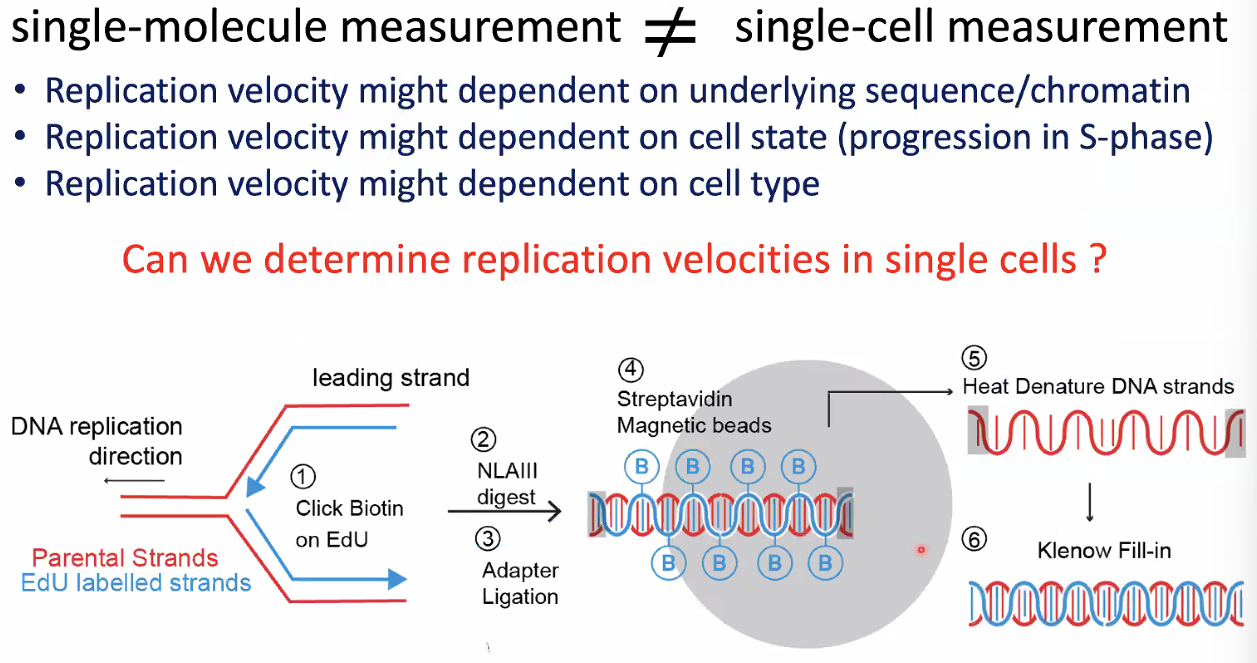
single-molecule measurement differs from single-cell measurement
![image-20221014153556341]()
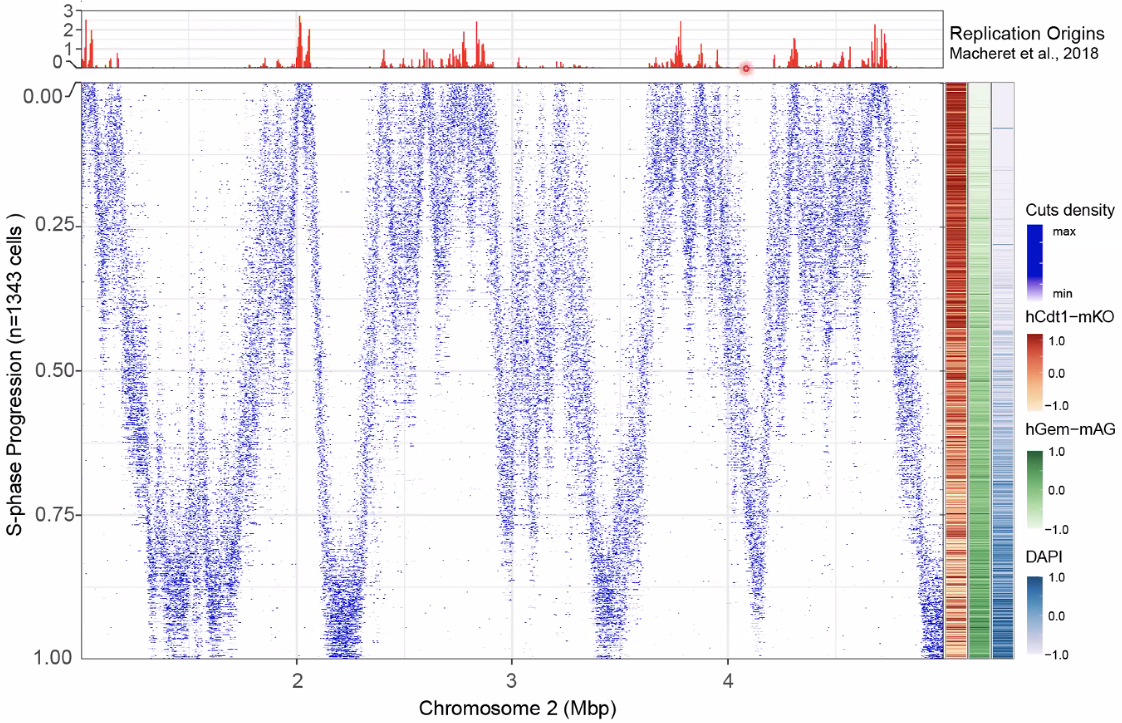
scEdUseq: single-cell measurement replication speed
![image-20221014153722898]()
concord with previous repilcation start sites
![image-20221014153907123]()
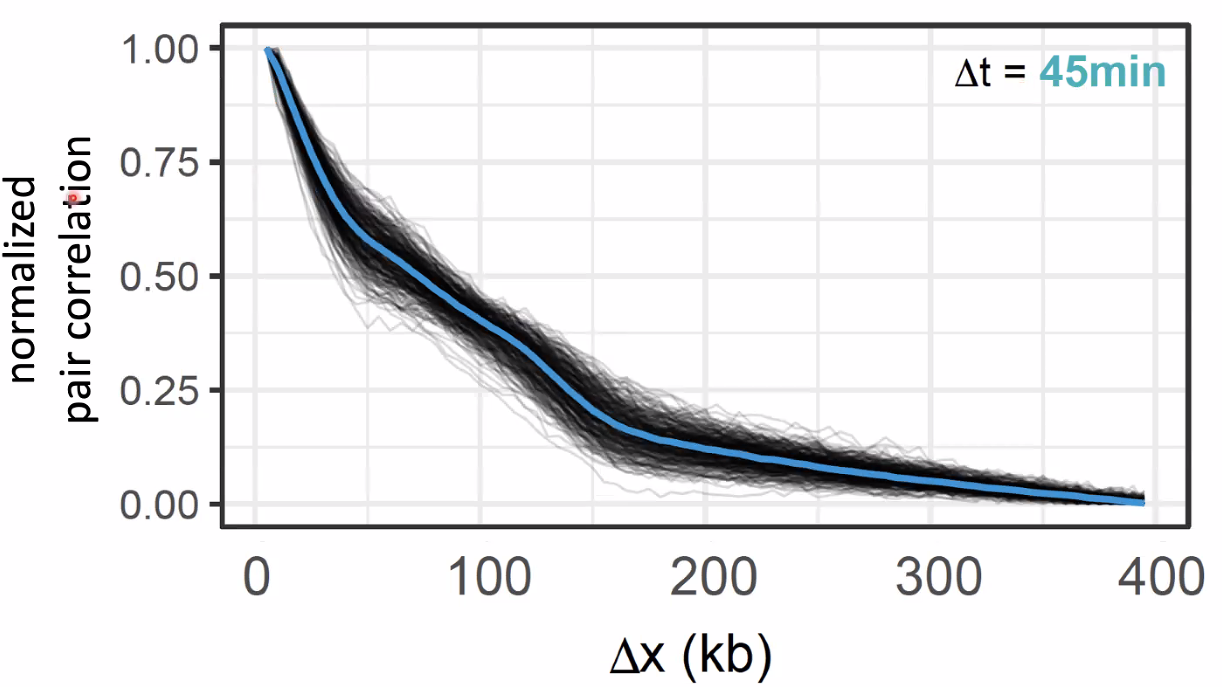
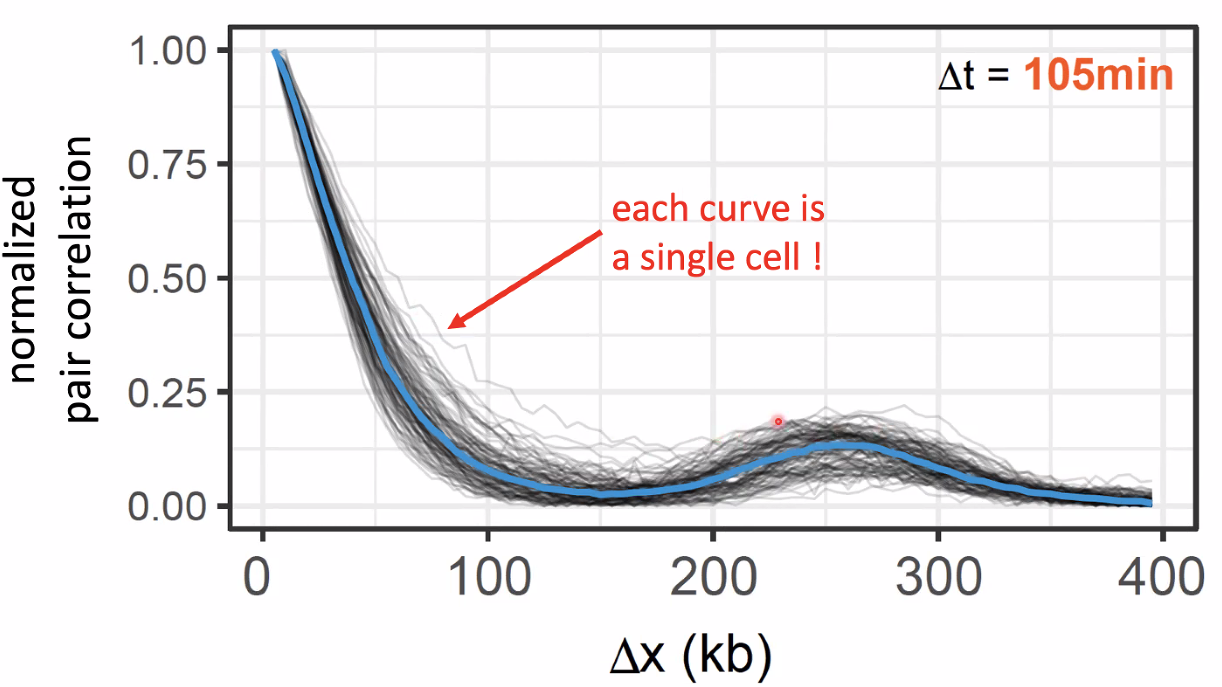
single pulse and pair pulse
![image-20221014154313554]()
![image-20221014154355545]()
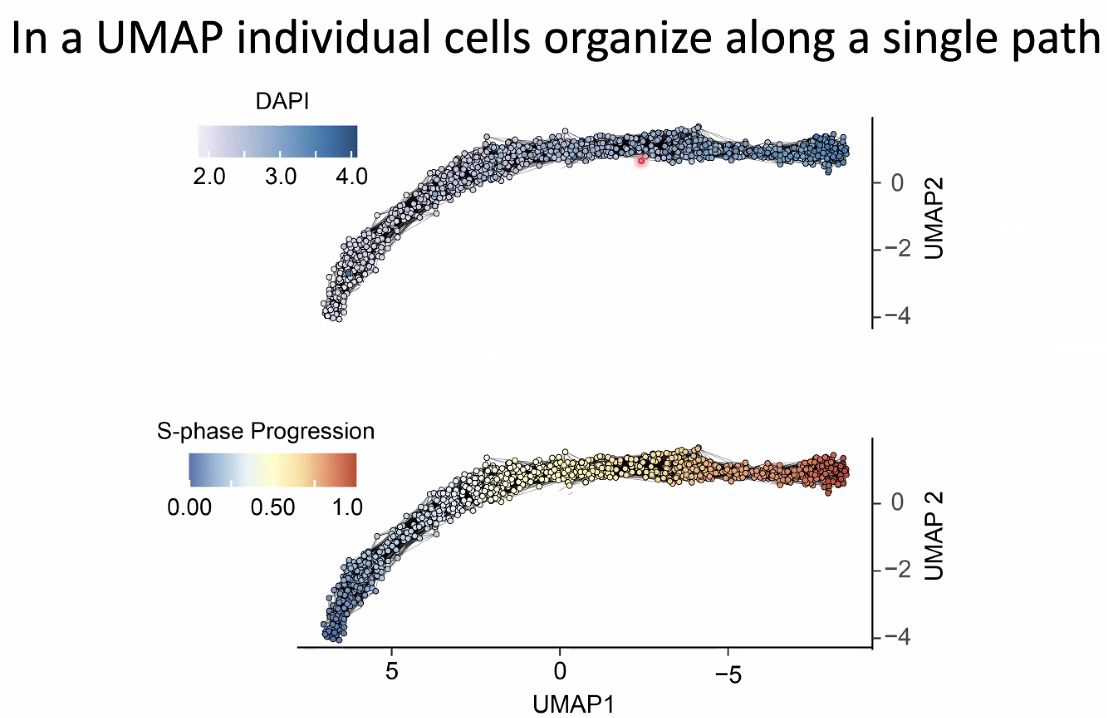
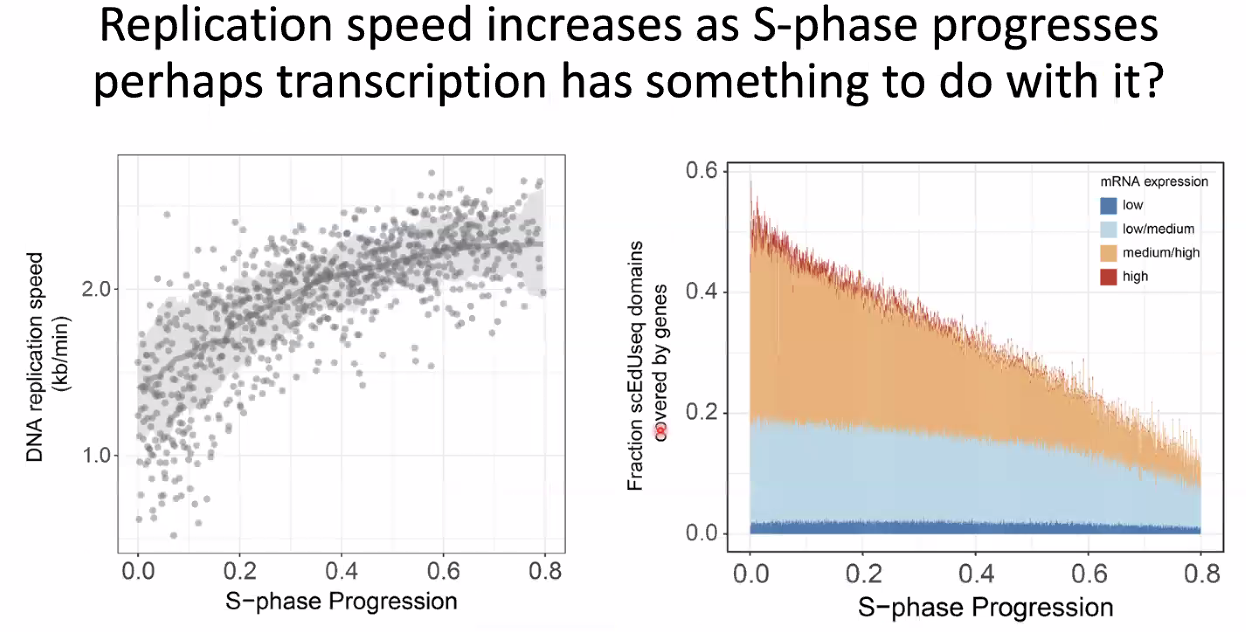
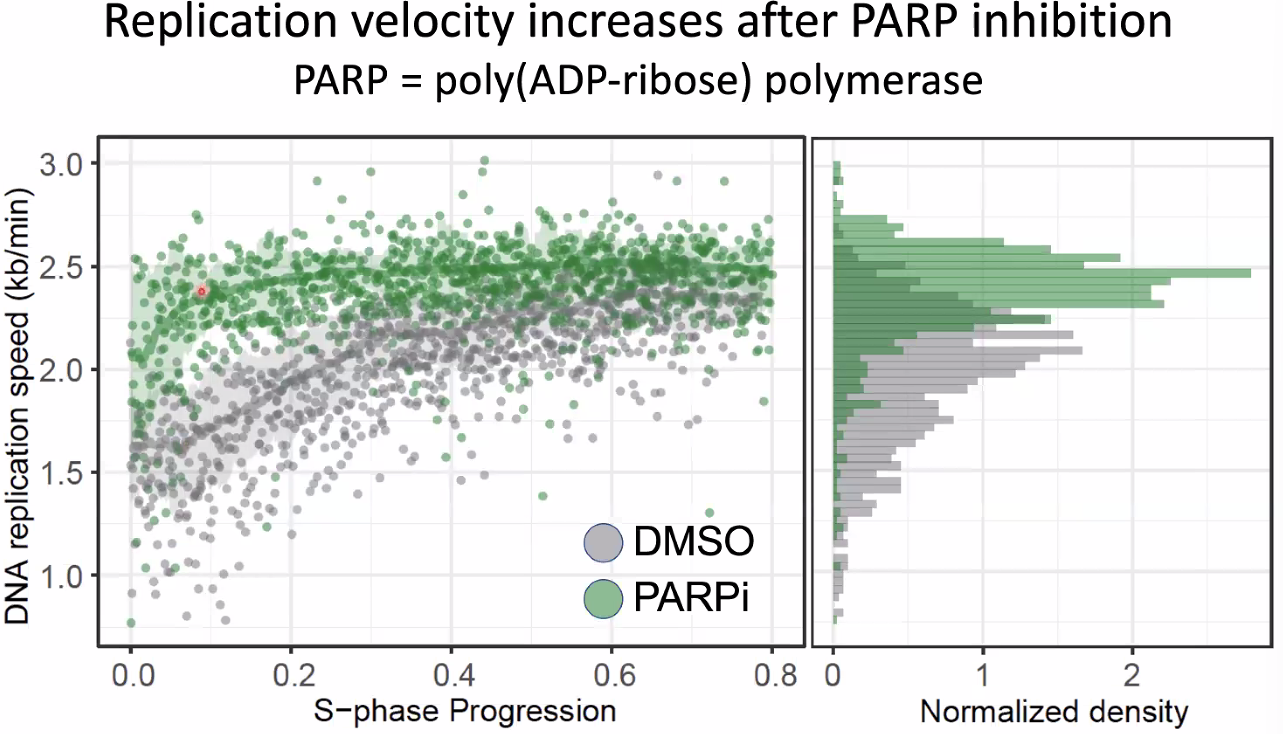
replication velocity increase with s-phase progression
![image-20221014154554385]()
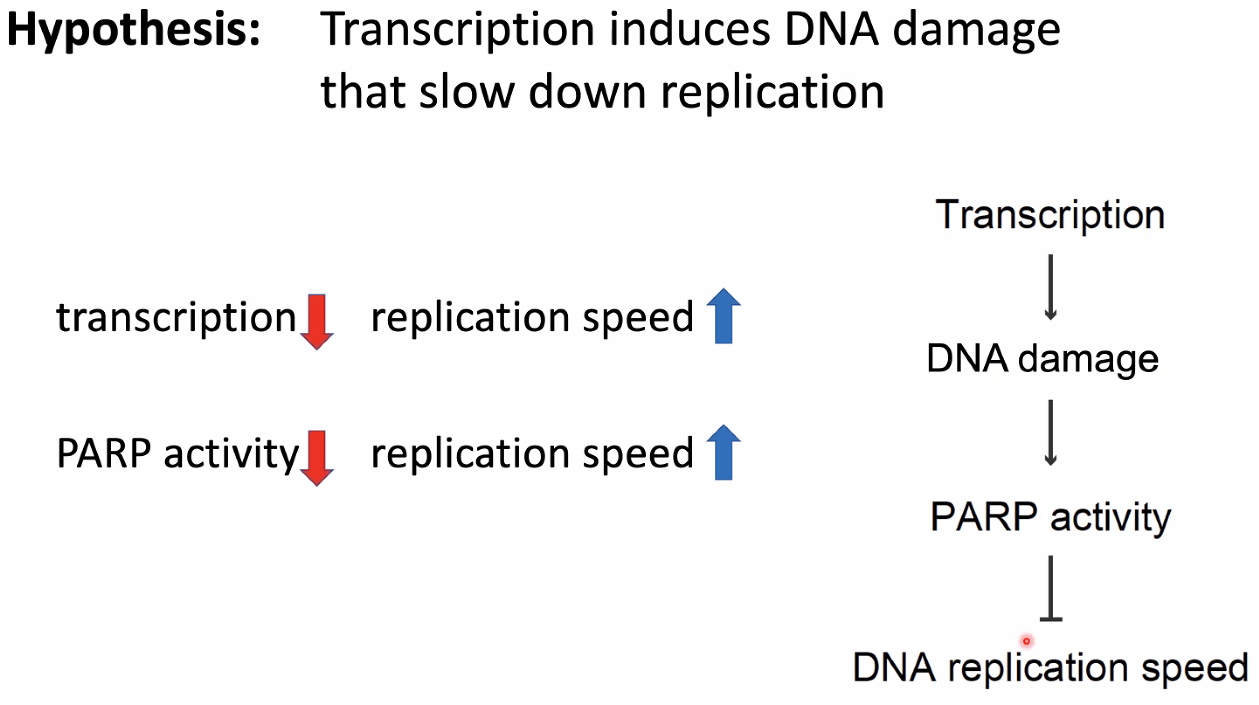
this might be correlated with transcription (increase after inhibition)
![image-20221014154731763]()
mechanism:
hyposis:
![image-20221014154825042]()
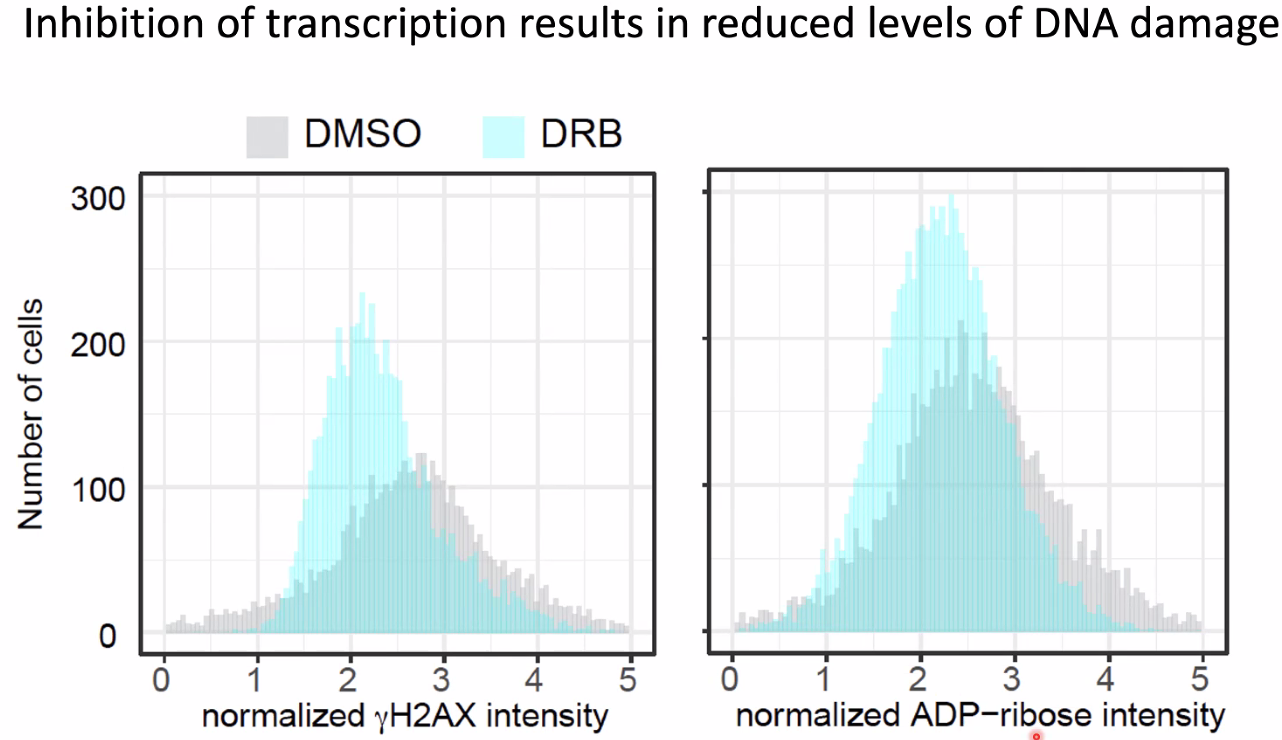
inhibit transcription lead to increased DNA damage
![image-20221014154851696]()
conclusions
![image-20221014155141927]()
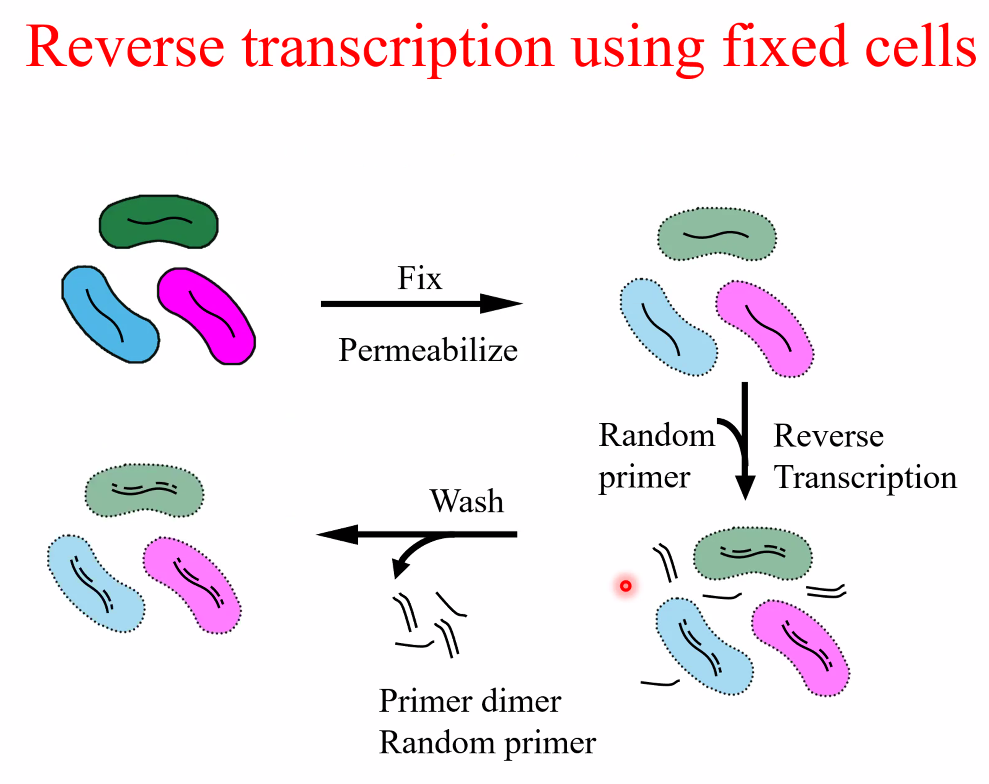
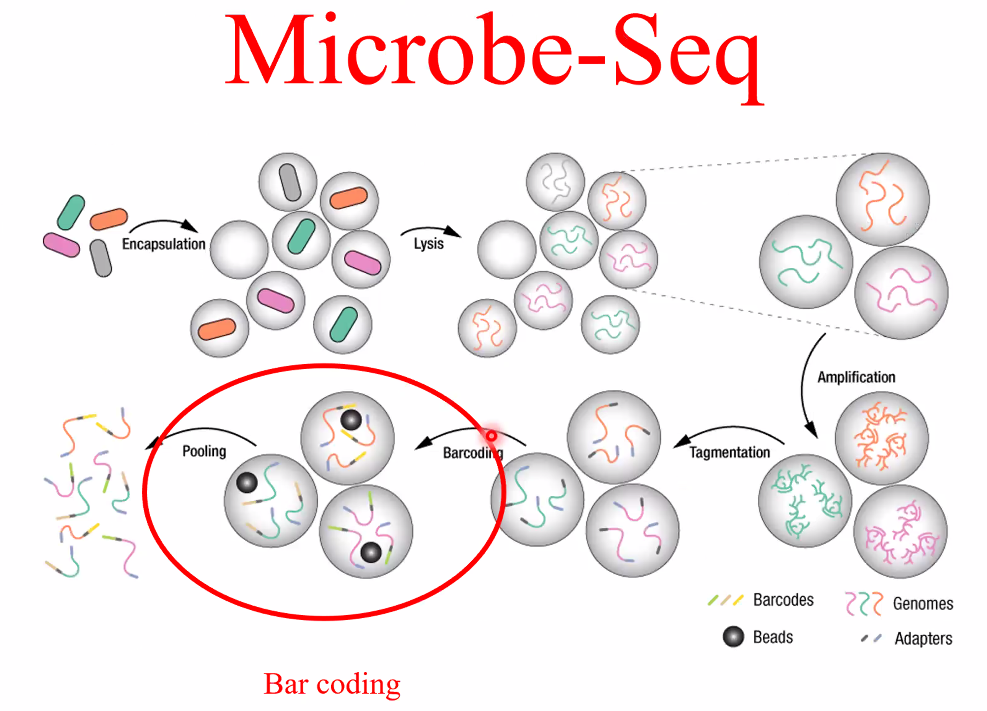
David Weitz: Applications of Single Microbe Sequencing
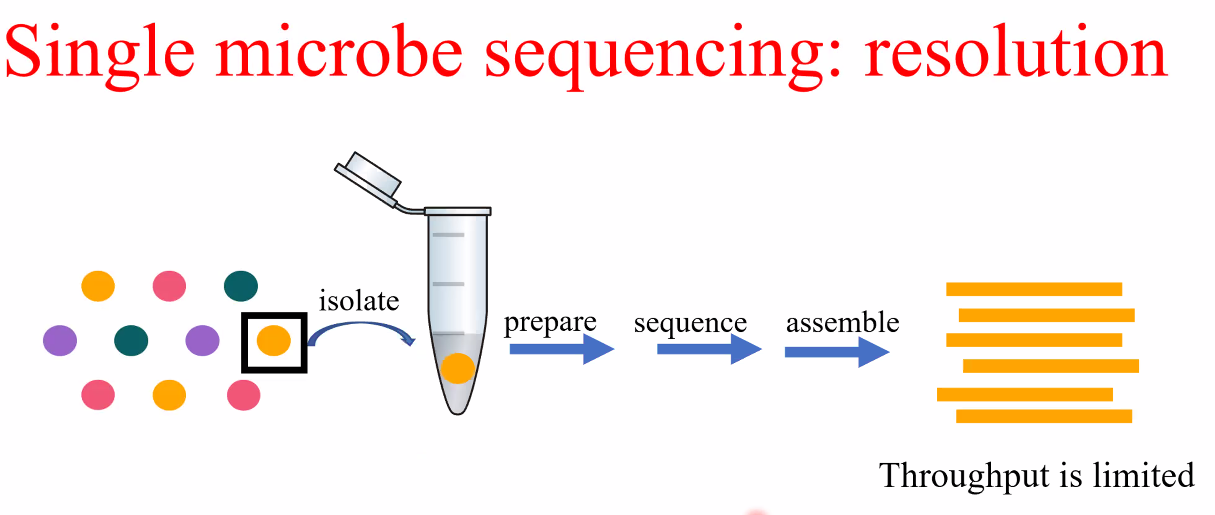
background: single microbe sequencing
![image-20221014160623546]()
Msc RNA-seq(fixed cells)
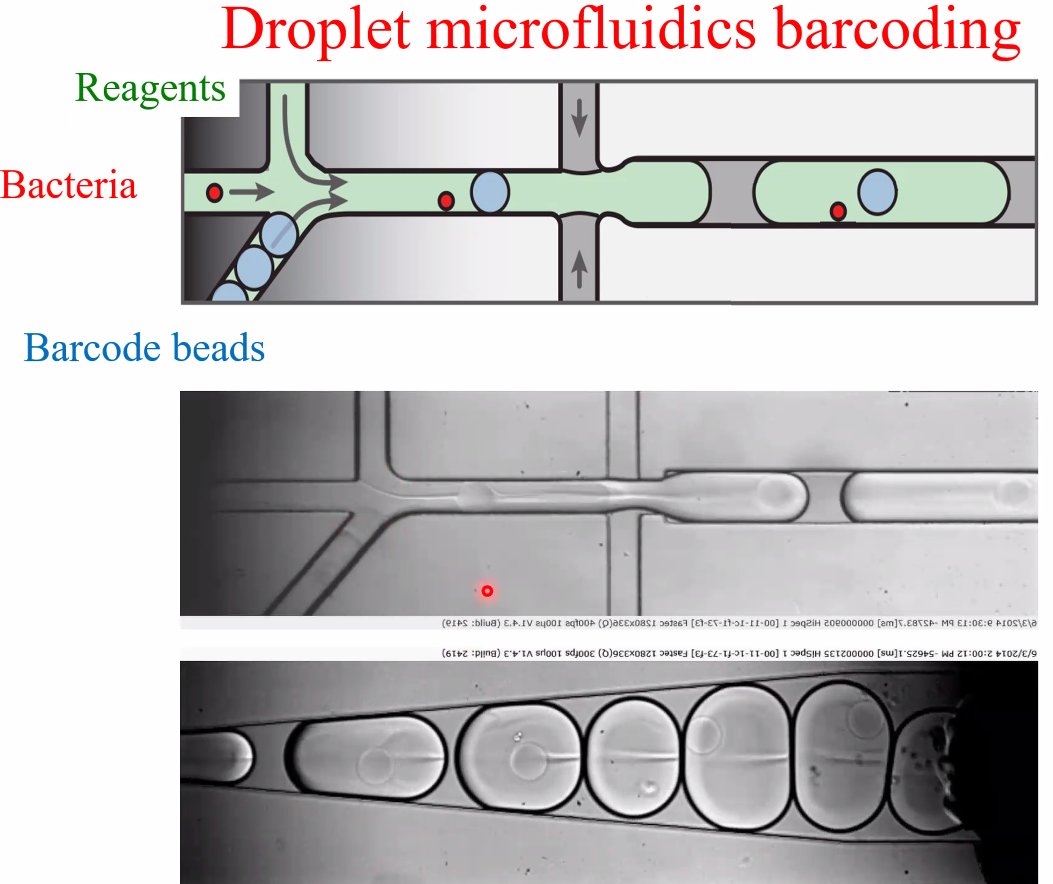
workflow
![image-20221014160842215]()
single-cell selection:
![image-20221014160952722]()
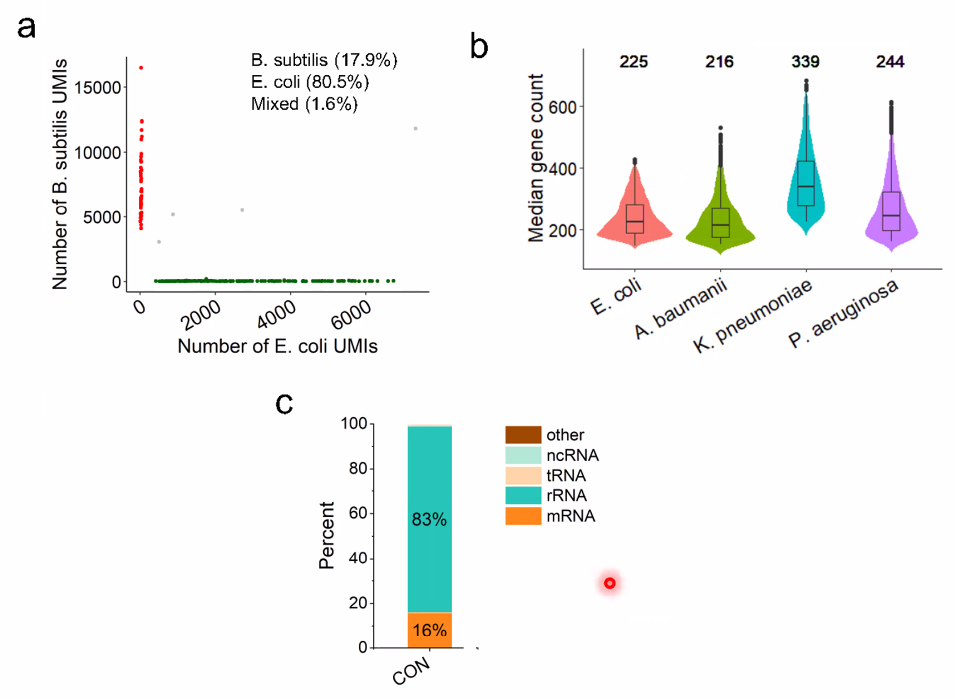
performance:
![image-20221014161137818]()
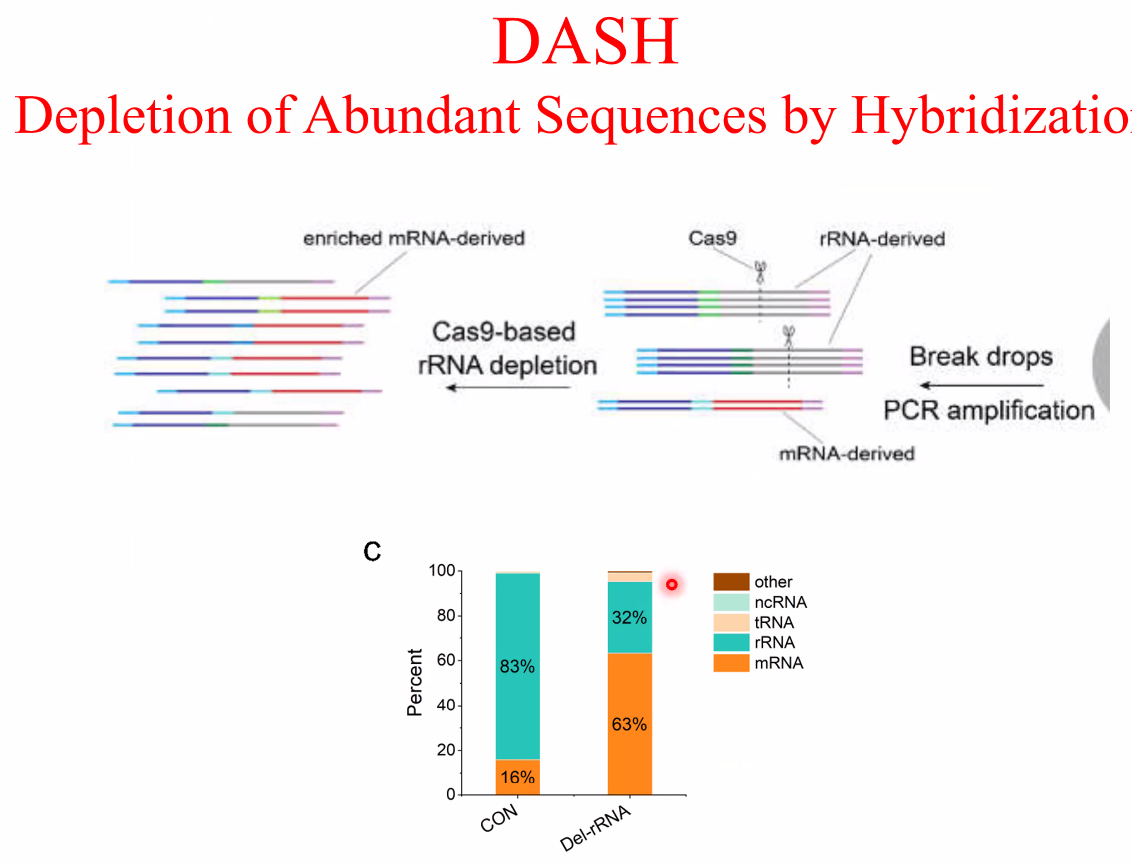
filter out rRNA using DASH
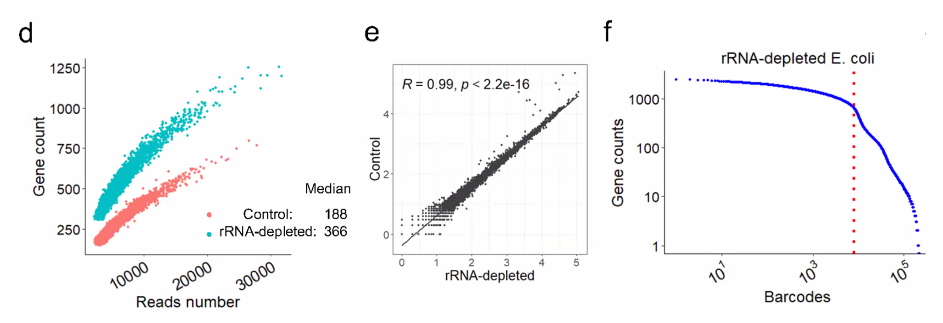
![image-20221014161236942]()
![image-20221014161303916]()
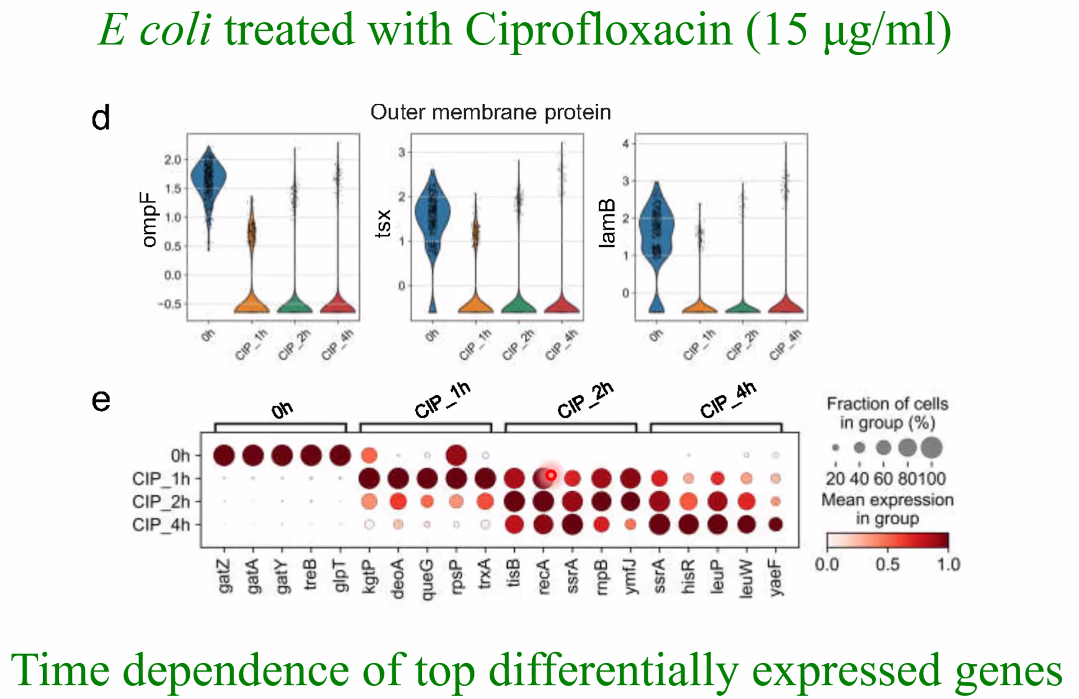
biological question: drug treatment of E coli, time series
![image-20221014161542168]()
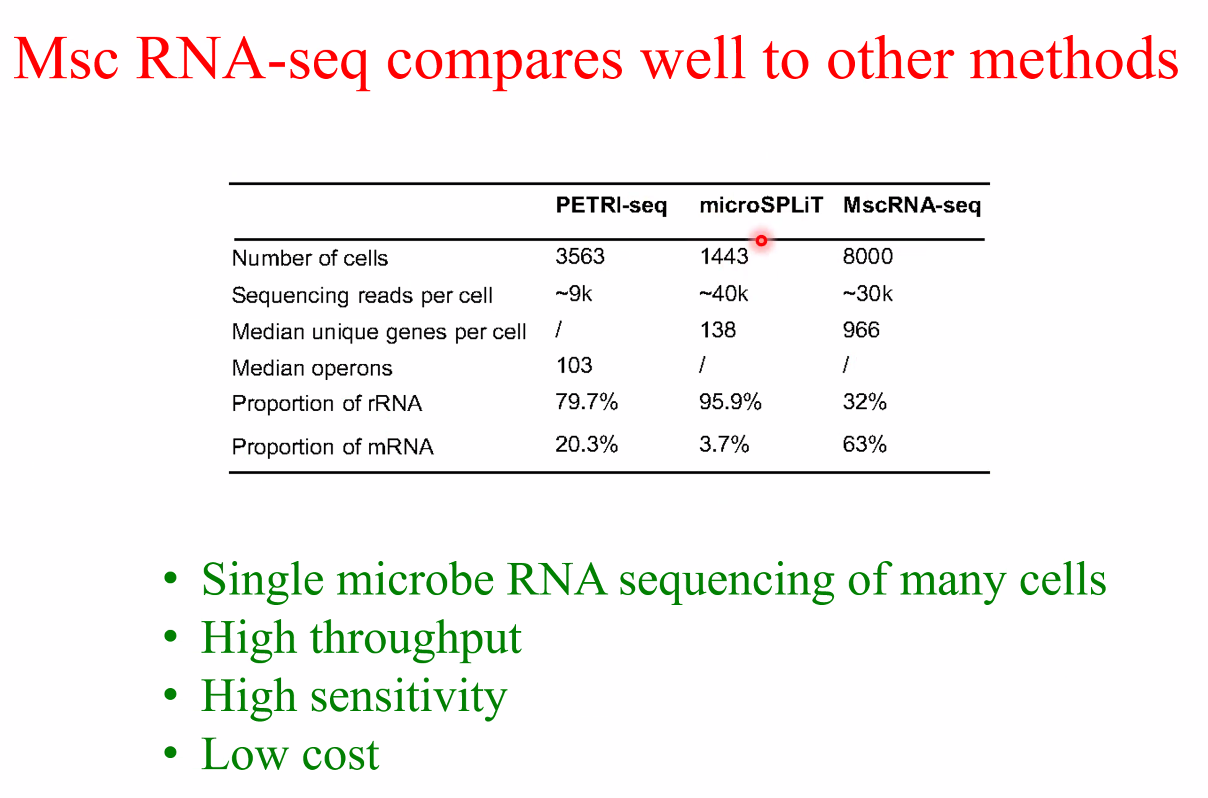
benchmark
![image-20221014161745227]()
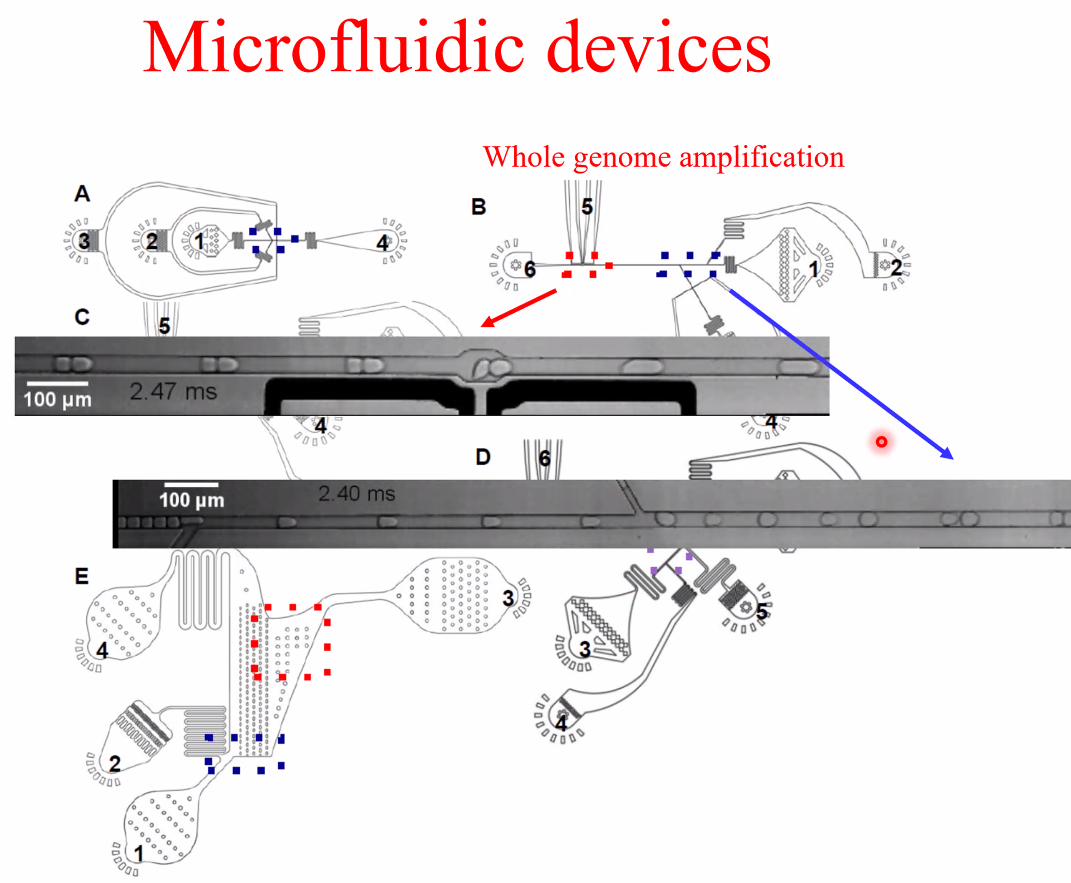
Microbe-Seq genome sequencing
![image-20221014162037046]()
work flow
![image-20221014161945581]()
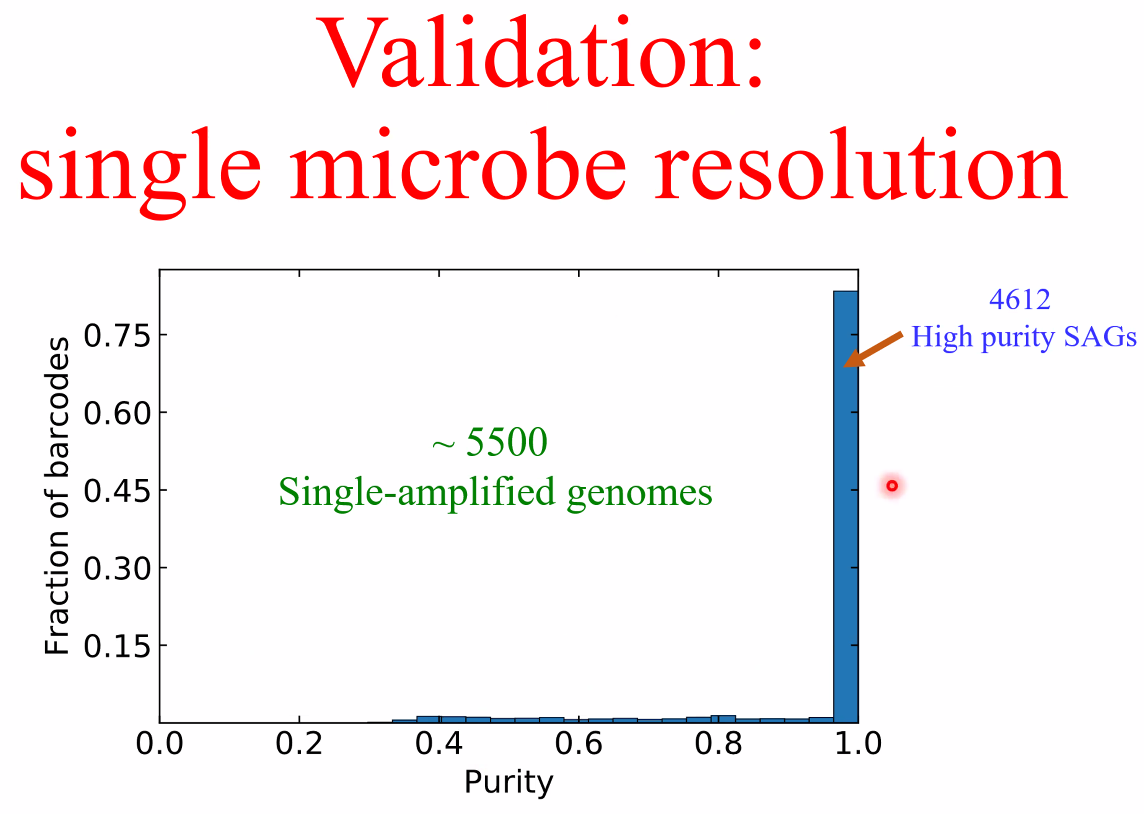
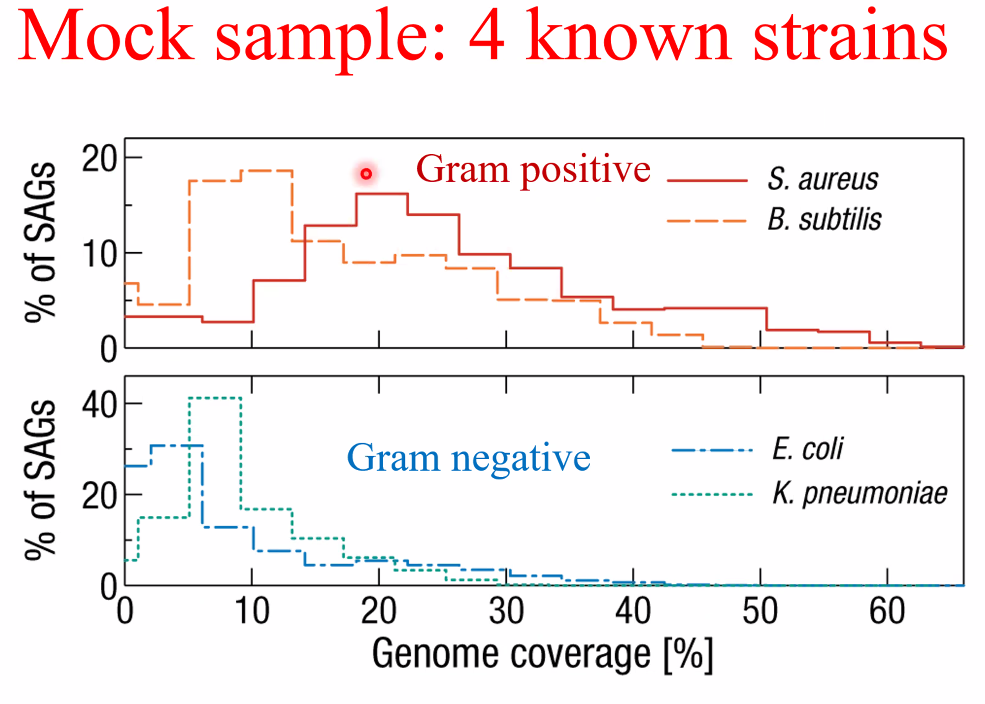
performance
![image-20221014162153557]()
![image-20221014162159169]()
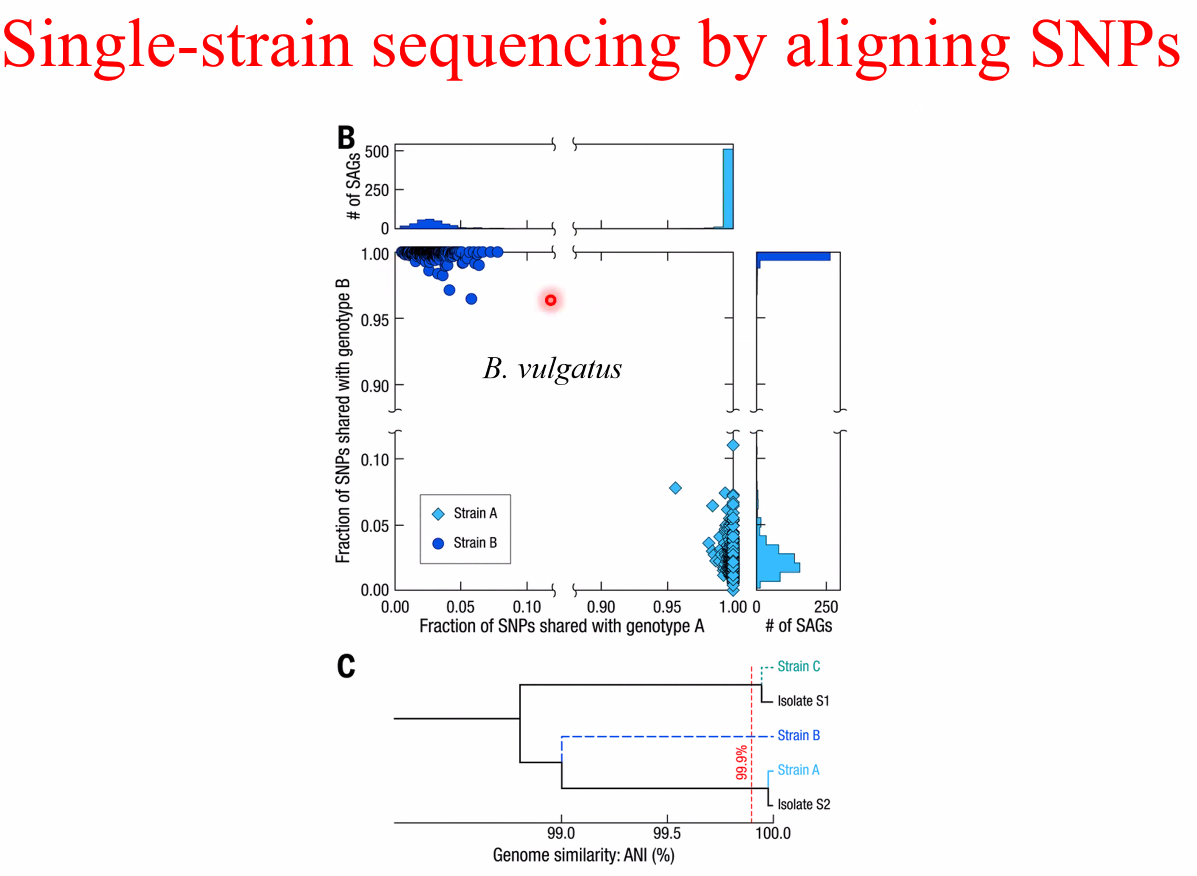
single-strain sequencing
![image-20221014162449709]()
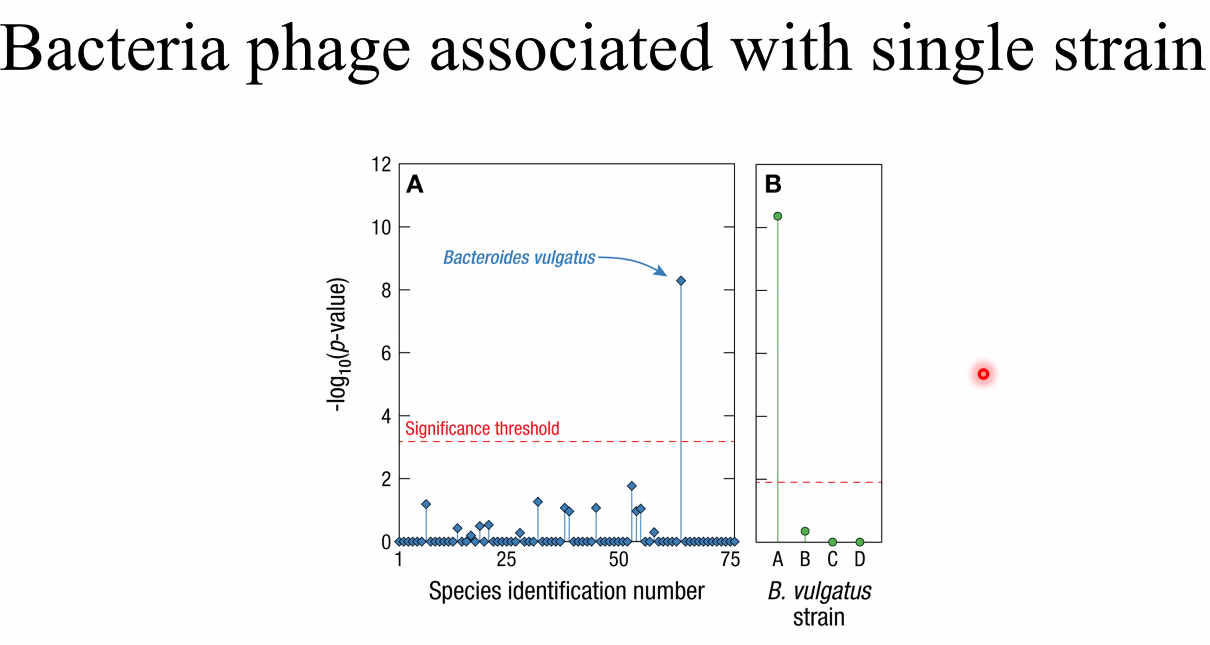
phages associated with strain
![image-20221014162709883]()
Amos Tanay: Single Cell Models for Deciphering the Birth of Cell-type Specific Epigenetics During Gastrulation
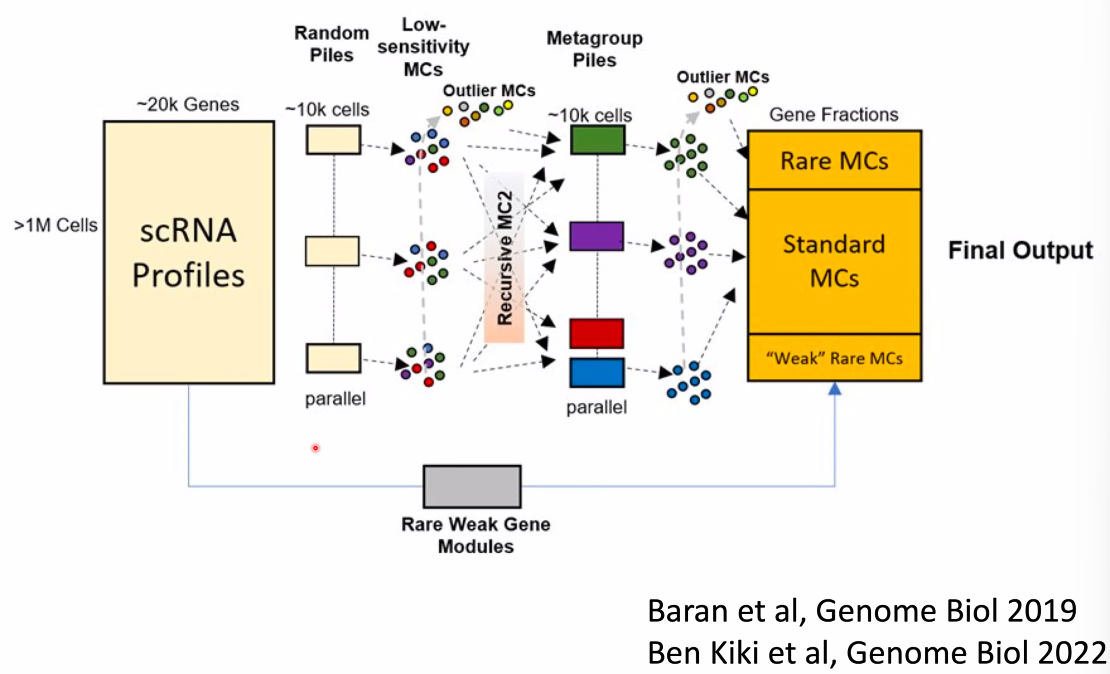
What is an atlas?
- dimensional reduction embeddings?
- gene expression profiles?
- A group of linked quantitative distributions over all genes !
![image-20221014163916493]()
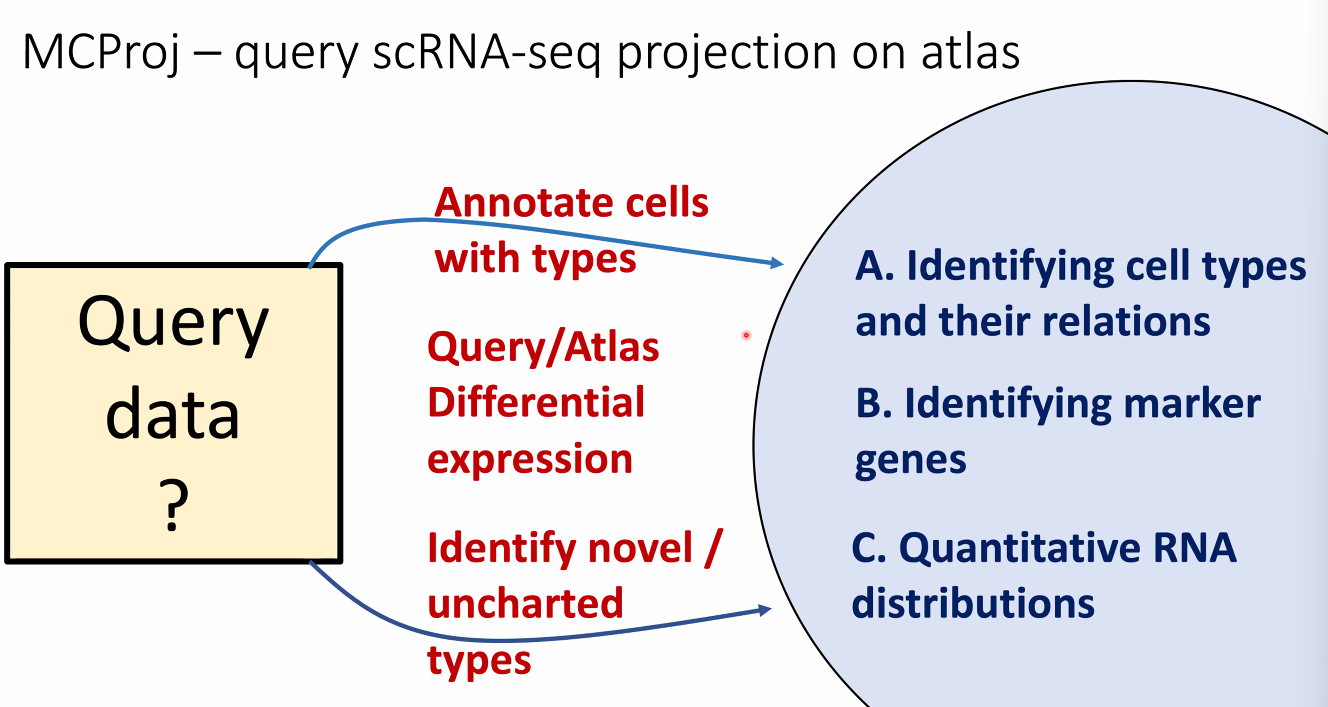
how to use atalses in 2020: query projection on atlas
![image-20221014164014068]()
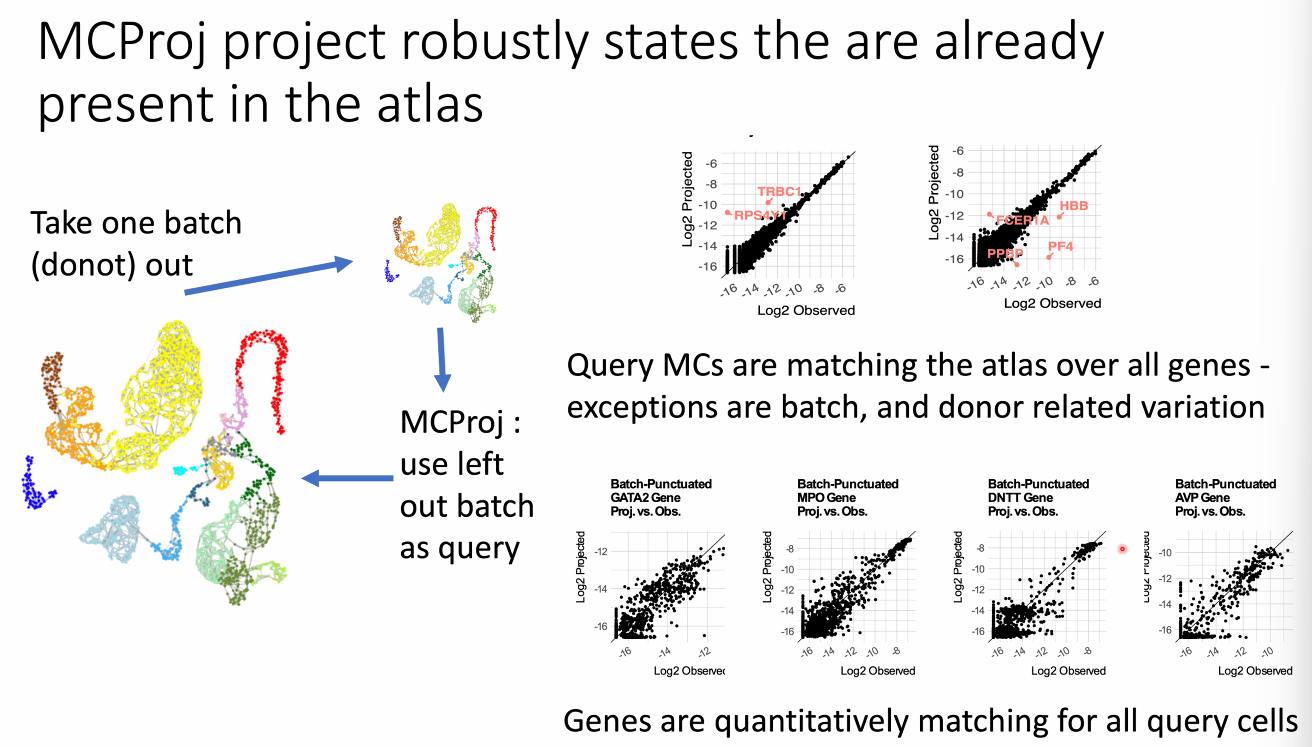
for known cell types:
![image-20221014164445876]()
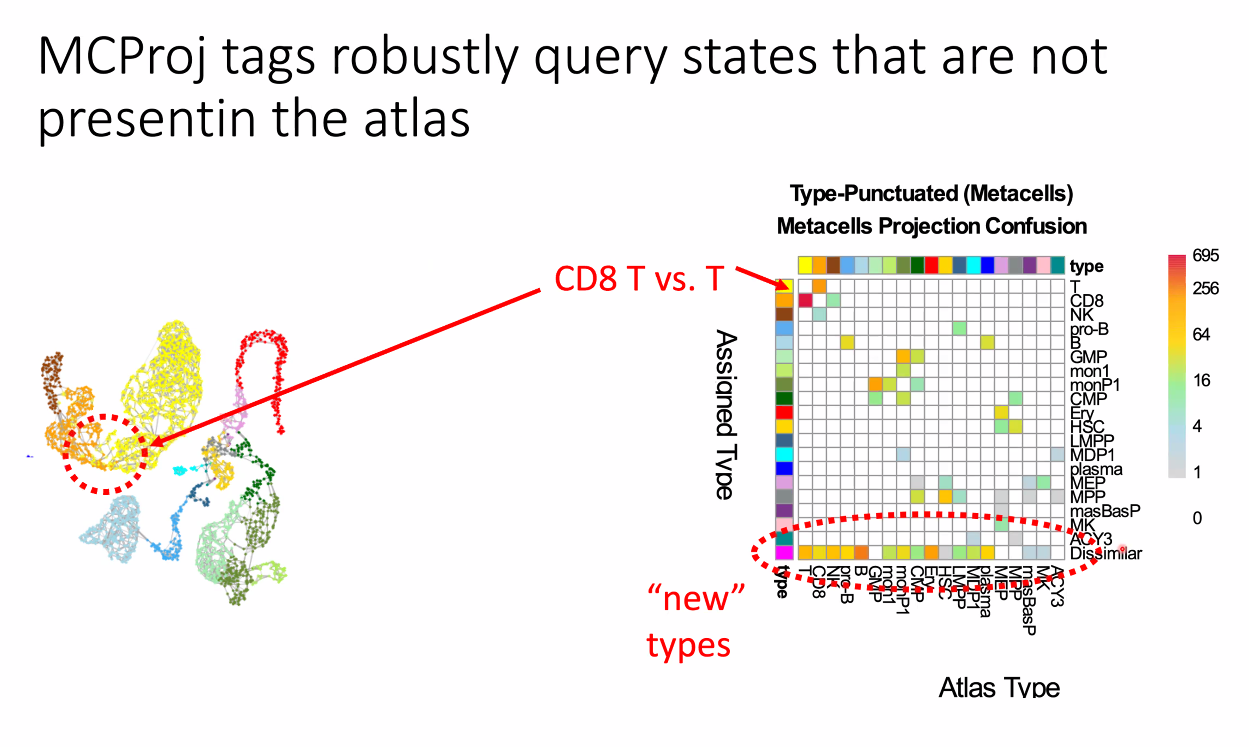
for novel cell types:
![image-20221014164504959]()
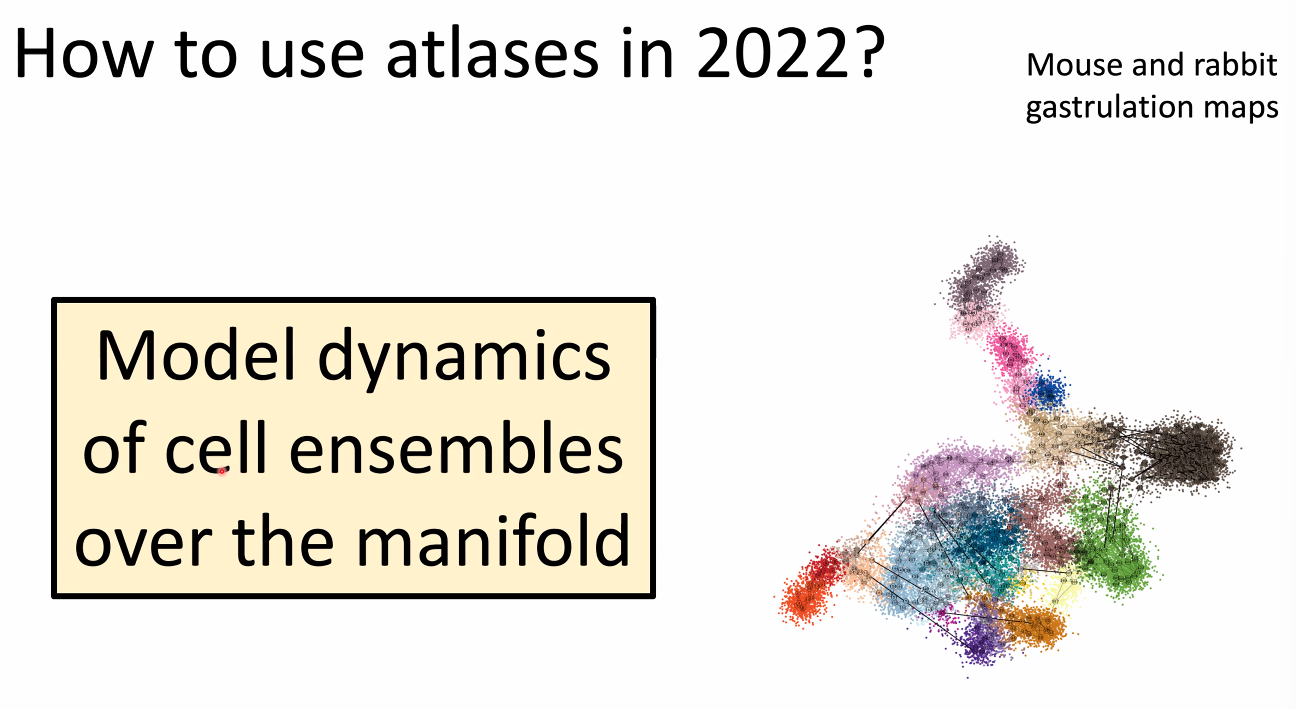
how to use atlas in 2022: model dynamics of cells.
![image-20221014164845083]()
Ge Gao: Rationally Design Generative Models for Delineating the Regulator Map in silico
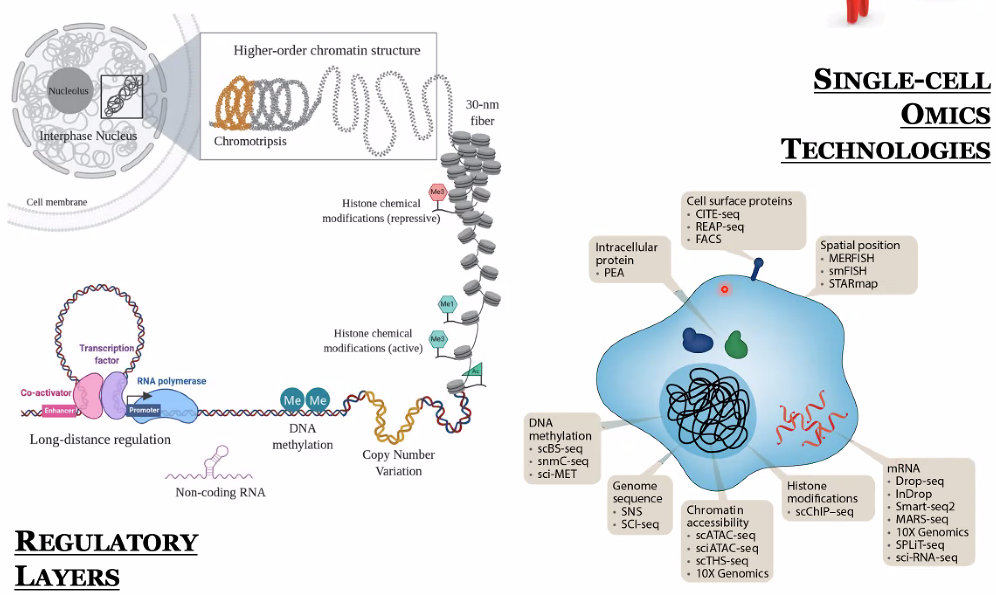
background: gene expression regulation
![image-20221014170755658]()
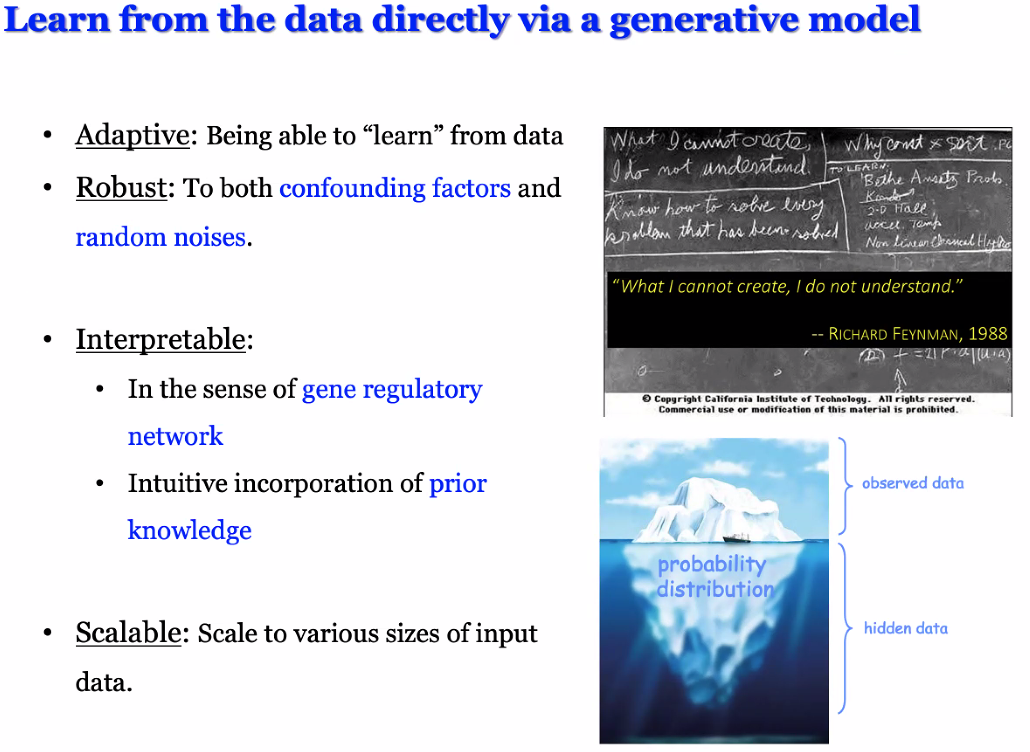
intuition: learn the regulating mechanisms from data
![image-20221014171047147]()